基于 kubesphere 和 kubeedge 在 Jetson 上运行 GPU 应用(docker/containerd)
在轨验证方案
应用的部署流程图
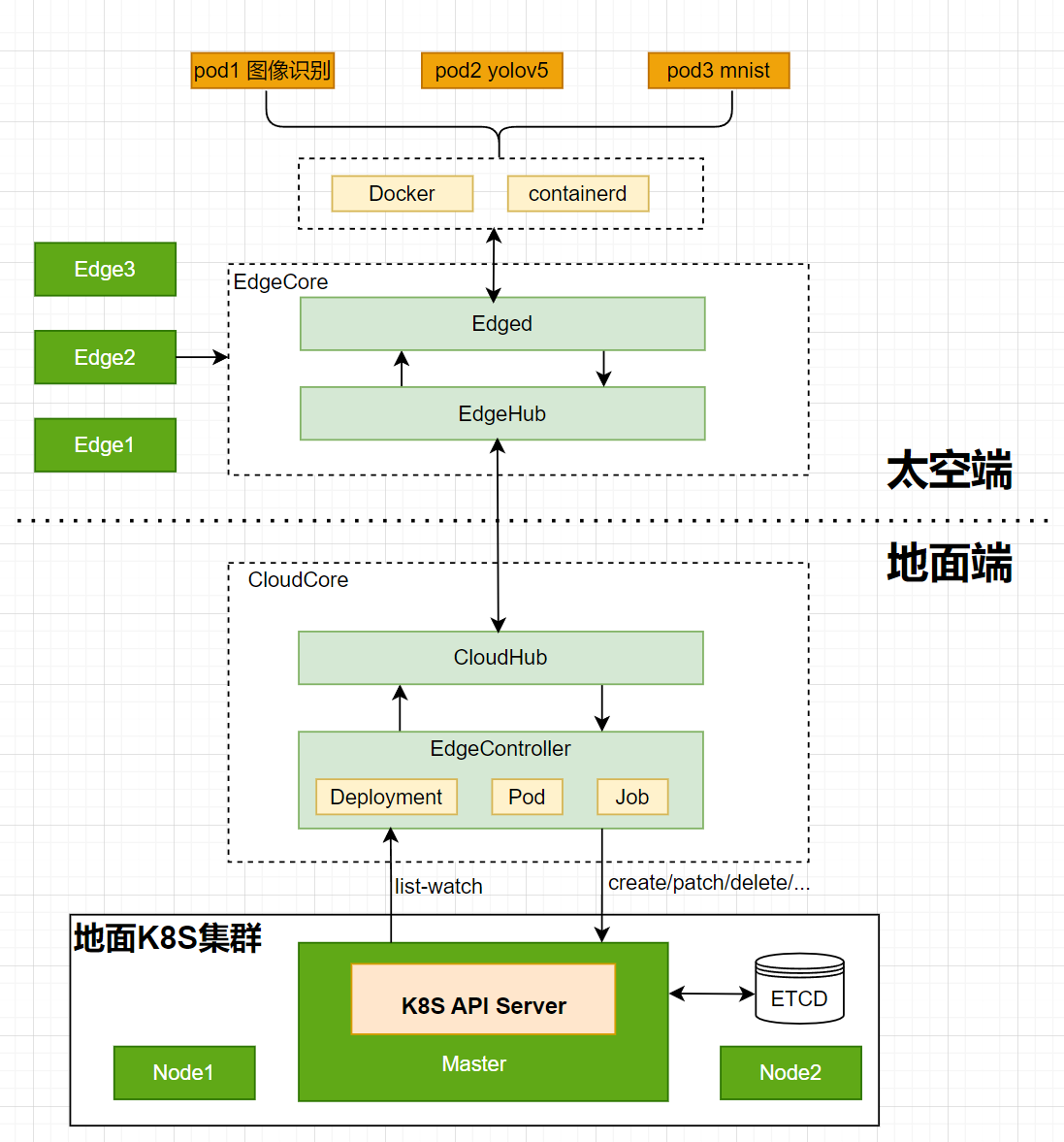
在 Jetson 上 如果部署 GPU 类型的应用,需要有 NVIDIA Container Runtime 支持。

环境配置
各个组件的版本信息如下:
| 组件 | 版本 |
|---|---|
| kubesphere | 3.4.1 |
| containerd | 1.7.2 |
| k8s | 1.26.0 |
| kubeedge | 1.15.1 |
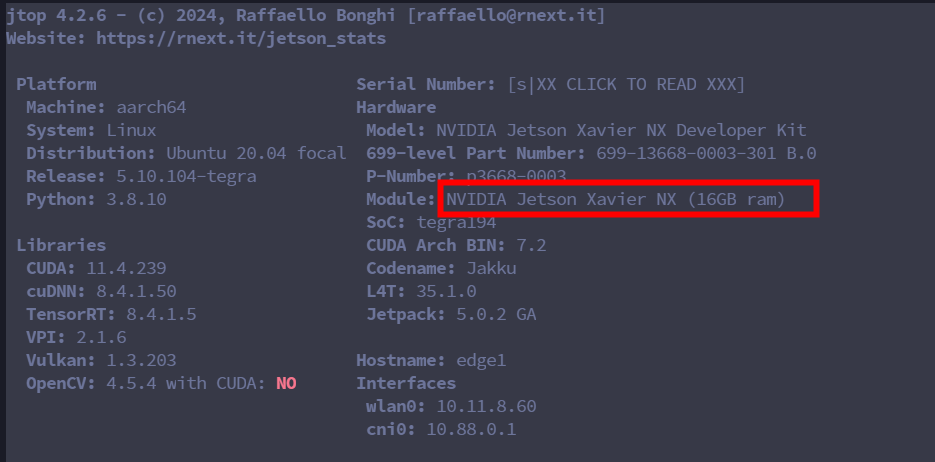
| Jetson型号 | NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX (16GB ram) |
| Jtop | 4.2.7 |
| JetPack | 5.1.3-b29 |
| docker | 24.0.5 |
安装jtop
安装 jtop 的目的是为了监控 GPU 的使用情况
|
|
安装JetPack
- 什么是 JetPack (https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/develop/software)
The Jetson software stack begins with NVIDIA JetPack™ SDK, which provides Jetson Linux, developer tools, and CUDA-X accelerated libraries and other NVIDIA technologies.
JetPack enables end-to-end acceleration for your AI applications, with NVIDIA TensorRT and cuDNN for accelerated AI inferencing, CUDA for accelerated general computing, VPI for accelerated computer vision and image processing, Jetson Linux API’s for accelerated multimedia, and libArgus and V4l2 for accelerated camera processing.
NVIDIA container runtime is also included in JetPack, enabling cloud-native technologies and workflows at the edge. Transform your experience of developing and deploying software by containerizing your AI applications and managing them at scale with cloud-native technologies.
Jetson Linux provides the foundation for your applications with a Linux kernel, bootloader, NVIDIA drivers, flashing utilities, sample filesystem, and toolchains for the Jetson platform. It also includes security features, over-the-air update capabilities and much more.
JetPack will soon come with a collection of system services which are fundamental capabilities for building edge AI solutions. These services will simplify integration into developer workflows and spare them the arduous task of building them from the ground up.
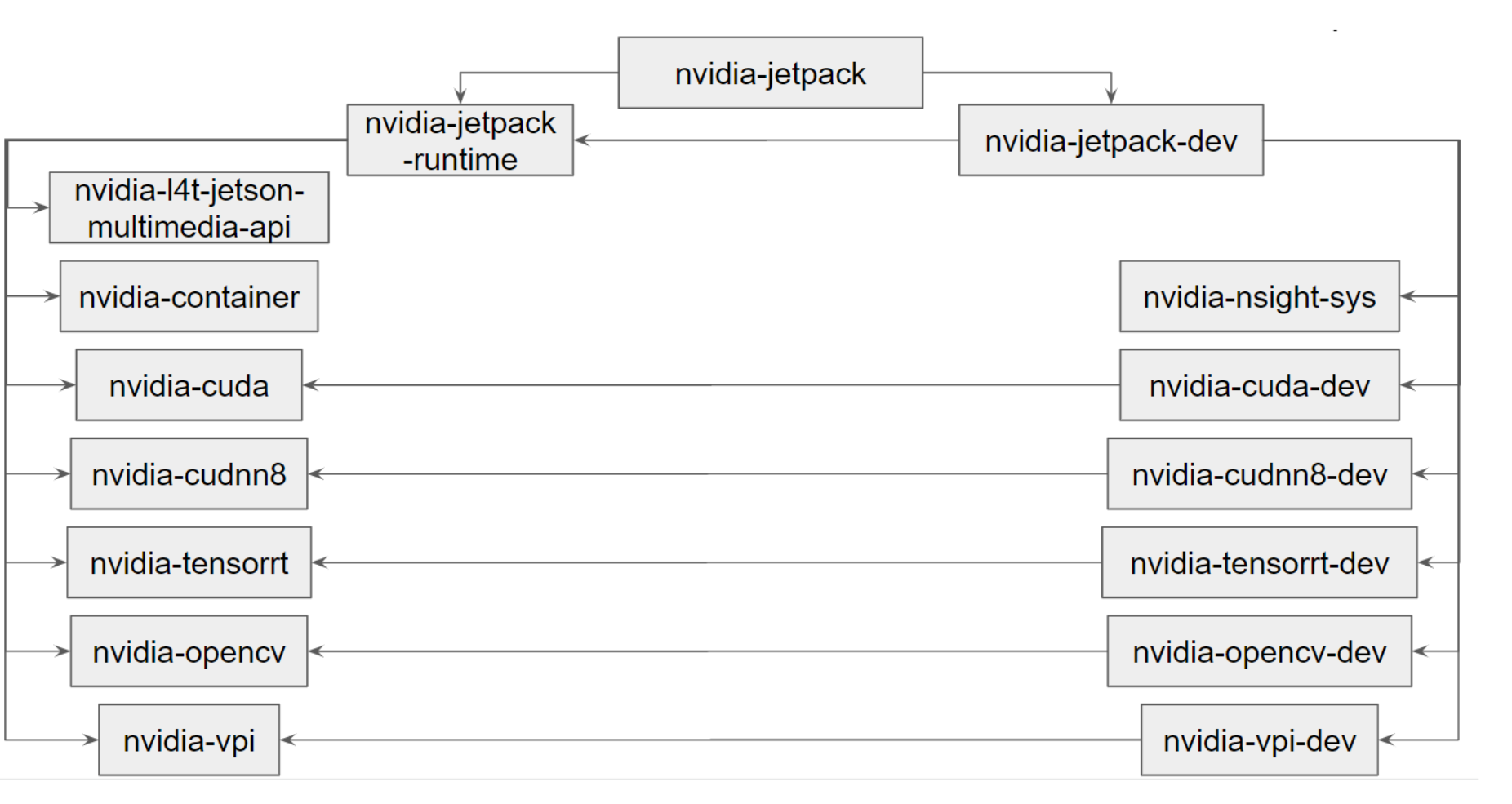
- JetPack 组成
- 安装命令
|
|
参考文档:NVIDIA JetPack Documentation
- 无法安装,请更换镜像源
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8Please edit your nvidia-l4t-apt-source.list to r34.1: deb https://repo.download.nvidia.com/jetson/common r34.1 main deb https://repo.download.nvidia.com/jetson/t234 r34.1 main Run below command to upgrade and install sdk components: sudo apt dist-upgrade sudo reboot sudo apt install nvidia-jetpack
地卫二 Jetson安装组件版本信息

-
nvidia-ctk 版本信息:NVIDIA Container Toolkit CLI version 1.11.0-rc.1
-
jetpack 版本信息

Nvida 官方的机器学习 docker 镜像
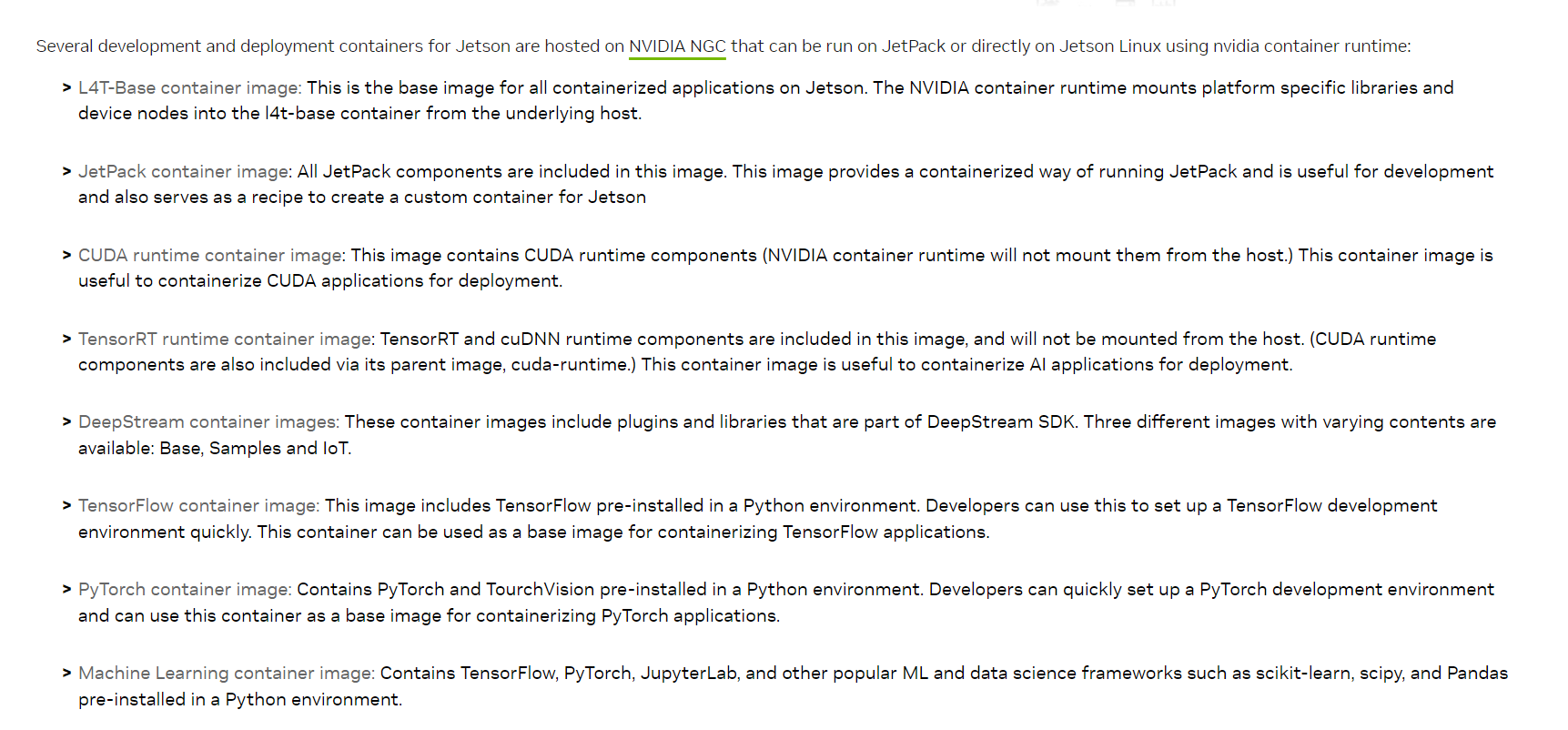
其中 l4t-base container 是基础镜像,可以在此基础上构建自己所需的镜像。
例如:
|
|
配置 GPU 容器运行时 和 nvdia k8s device plugin
dokcer run 或者 ctr run 部署的配置
-
docker:vim /etc/docker/daemon.json
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10{ "runtimes": { "nvidia": { "path": "nvidia-container-runtime", "runtimeArgs": [] } }, "default-runtime": "nvidia" } -
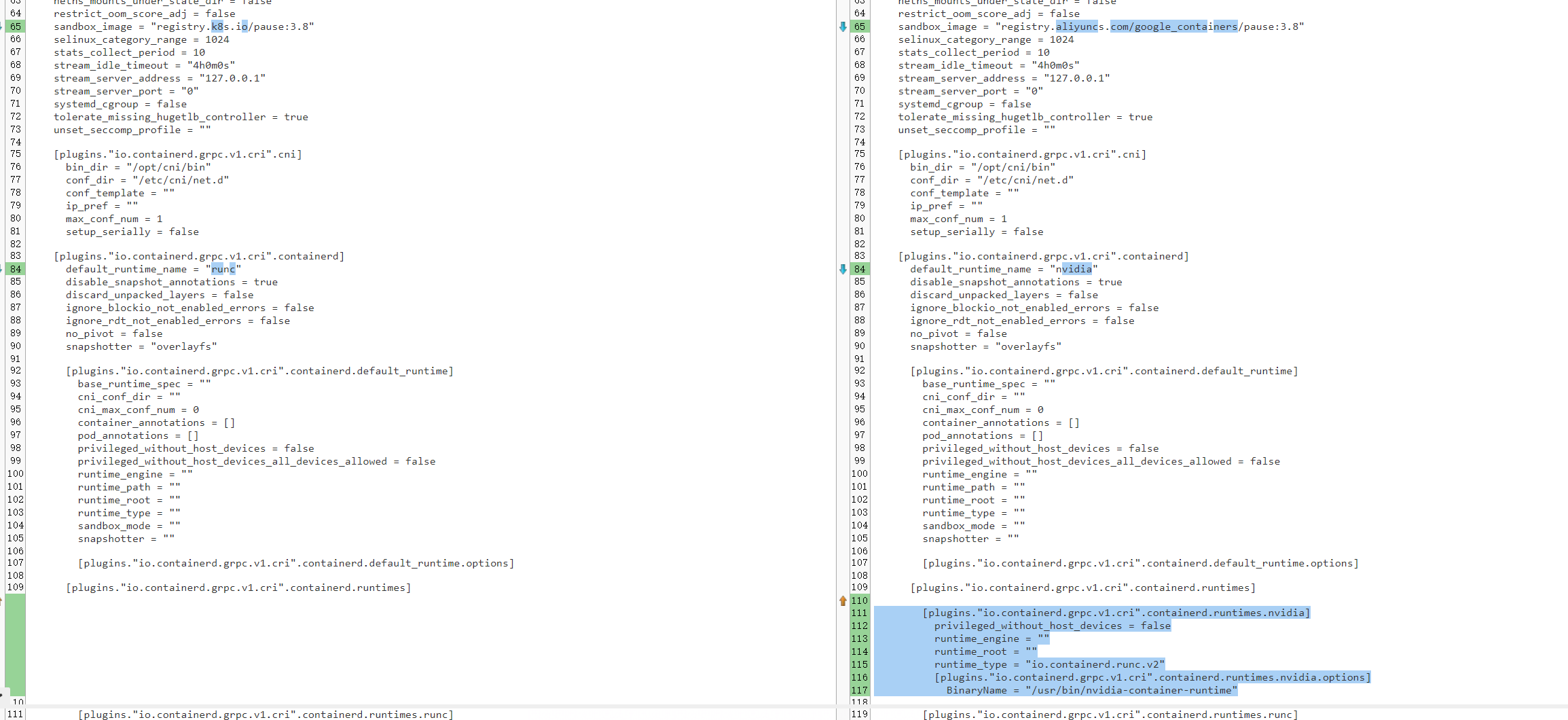
containerd:vim /etc/containerd/config.toml
修改runtime插件的配置,首先切换到runtime v2
1 2 3[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes] [plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc] runtime_type = "io.containerd.runc.v2"将CRI配置中的runc binary改为
nvidia-container-runtime1 2 3[plugins."io.containerd.runtime.v1.linux"] shim = "containerd-shim" runtime = "nvidia-container-runtime" # 将此处 runtime 的值改成 nvidia-container-runtime
k8s 部署配置
-
docker:vim /etc/docker/daemon.json
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10{ "runtimes": { "nvidia": { "path": "nvidia-container-runtime", "runtimeArgs": [] } }, "default-runtime": "nvidia" } -
containerd:vim /etc/containerd/config.toml
|
|
nvdia k8s device plugin 部署
配置虚拟化GPU个数
touch virtualization_configmap.yaml
|
|
部署 device plugin daemonSet
touch device-plugin.yaml
|
|
部署 mnist 算法
mnist 镜像准备
- pytorch 训练代码
|
|
-
Dockerfile 打镜像,基于 nvidia 的 pytorch 基础镜像
1 2 3FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/l4t-pytorch:r35.2.1-pth2.0-py3 COPY pytorch-mnist.py /home/
docker build -t mnist:1.0 .
容器部署
- docker 运行命令(不加 –runtime nvidia 参数,会使用 CPU 进行训练)
|
|
-
不打镜像直接挂载代码
1 2 3sudo docker run -it --rm --runtime nvidia --network host -v /home/user/project:/location/in/container nvcr.io/nvidia/l4t-pytorch:r35.2.1-pth2.0-py3 python3 pytorch-minst.py -
安装 Harbor 镜像仓库,直接 docker push 然后 ctr images pull 拉取镜像
-
containerd 运行命令:
|
|
pod部署
|
|
deployment 部署
|
|
部署GPU 虚拟化 应用
测试代码 test.py
|
|
pod 部署
- 单 GPU
|
|
参考文档
nvidia-ctk安装教程:Installing the NVIDIA Container Toolkit
安装有问题可以参考:Trobleshooting
