kubeEdge 代码解析
目录
beehive
beehive是一个基于go channel的消息框架,用于KubeEdge模块之间的通信。
beehive模块在整个kubeedge中扮演了非常重要的作用,它实现了一套Module管理的接口,程序中各个模块的启动、运行、模块间的通信等都是由其统一封装管理。
Beehive 模块是 kubeedge 的核心模块,它负责管理所有模块的启动与停止,同时也负责多模块间的通信,它当前主要由: model, context, socket, channel 四个部分组成,其中:
model 包
- model 部分定义了消息的模型,这个消息模型是各个组件间通信所必须符合的规范。 这里面定义了结构体 message ,message是 beehive 不同 module 之间通信的信息载体,包含三部分内容:消息头、消息路由、消息内容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
// Message struct
// model 包中定义了消息的模型, 其主要结构如下:
type Message struct {
Header MessageHeader `json:"header"`
Router MessageRoute `json:"route,omitempty"`
Content interface{} `json:"content"`
}
// MessageRoute contains structure of message
// 消息路由:消息路由中定义了消息的一些操作和目的地等信息,其结构如下:
type MessageRoute struct {
//消息的来源
Source string `json:"source,omitempty"`
//消息的目的地
Destination string `json:"destination,omitempty"`
//消息广播的时候需要广播到哪个组
Group string `json:"group,omitempty"`
//如何去操作资源
Operation string `json:"operation,omitempty"`
//想要操作的资源类型是什么
Resource string `json:"resource,omitempty"`
}
// MessageHeader defines message header details
// 消息头中主要定义了一些消息头部的详细信息,其结构如下:
type MessageHeader struct {
//消息的ID,使用UUID生成。
ID string `json:"msg_id"`
//消息的父ID,一般在响应消息时候填充,其一般要与请求消息的ID相同
ParentID string `json:"parent_msg_id,omitempty"`
//消息的创建时间
Timestamp int64 `json:"timestamp"`
//消息的特定资源版本,目前保存的是 k8s 资源的版本。
//kubeedge利用消息资源版本的概念来实现可靠传输。
ResourceVersion string `json:"resourceversion,omitempty"`
//发送同步的标志位,该标志将在 sendsync 中设置。
Sync bool `json:"sync,omitempty"`
//船渡消息的类型,一般为 channel,unixsocket 等类型,如果为空,则默认是 channel 类型
MessageType string `json:"type,omitempty"`
}
|
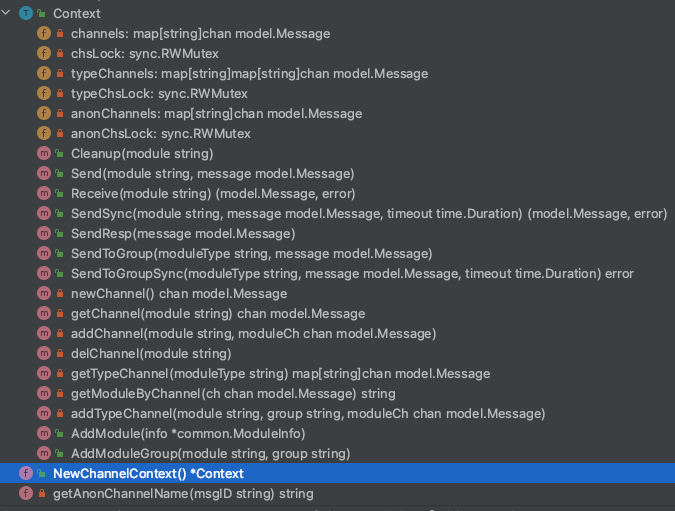
context 包
-
context 部分定义了消息的上下文以及模块上下文两个接口,同时使用了一个全局上下文来管理各个类型的上下文。
-
model 管理 和 message消息通信管理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
// ModuleContext is interface for context module management
// ModuleContext 接口定义了如何将 module 加入到当前 context, 并将其分组,以及,结束时如何清理模块的接口:
type ModuleContext interface {
AddModule(info *common.ModuleInfo)
AddModuleGroup(module, group string)
Cleanup(module string)
}
// MessageContext is interface for message syncing
// MessageContext 接口定义了上下文如何为各个模块发送,接收,同步以及广播消息:
type MessageContext interface {
// async mode
Send(module string, message model.Message) //发送同步消息到指定 module
Receive(module string) (model.Message, error) // 接受发送到指定 module的消息
// sync mode
SendSync(module string, message model.Message, timeout time.Duration) (model.Message, error) //发送同步消息到指定的 module
SendResp(message model.Message) //发送对同步消息的响应
// group broadcast
SendToGroup(group string, message model.Message) // 发送异步消息到指定的 group 下的所有module
SendToGroupSync(group string, message model.Message, timeout time.Duration) error // 发送同步消息到指定的 group 下的所有module
}
|
当前这个两个接口的实现,在 kubeedge 中,主要是由 socket 部分和 channel 部分对其进行了实现,分别用于远程模块通信与本地模块通信。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
// 全局上下文 主要是给本地的上下文通信,
// 单例模式,启动就只存在一份。
var (
// singleton
globalContext *GlobalContext
once sync.Once
)
// GlobalContext 主要用来管理 module , message 与 Context 间的关系,以及提供一些方法,来便捷的操作 context, 其主要结构如下:
// GlobalContext is global context: only use for local cache to dispatch message
type GlobalContext struct {
// 存储 context 类型与 ModuleContext 接口间关系
// key 为 context 类型,value 为对应的 ModuleContext 接口
moduleContext map[string]ModuleContext
// 存储 context 类型与 MessageContext 接口间关系
// key 为 context 类型,value 为对应的 MessageContext 接口
messageContext map[string]MessageContext
// 存储 module 与 context 类型间的关系
// key 为 module 名称,value 为对应的 context 类型
moduleContextType map[string]string
// 存储 group 与 context 类型间的关系
// key 为 group 名称,value 为对应的 context 类型
groupContextType map[string]string
ctx gocontext.Context
cancel gocontext.CancelFunc
ctxLock sync.RWMutex
}
|
方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
// 根据传入的 contextTypes 初始化 context
InitContext(contextTypes []string)
// 获取 context
GetContext() gocontext.Context
// 结束
Done() <-chan struct{}
// 取消
Cancel()
// 添加 module
AddModule(module *common.ModuleInfo)
// 添加 module group
AddModuleGroup(module, group string)
// 清理 module
Cleanup(module string)
// 发送消息到模块
Send(module string, message model.Message)
// 接收模块的消息
Receive(module string) (model.Message, error)
// 发送同步消息
SendSync(module string,message model.Message, timeout time.Duration)(model.Message, error)
// 发送响应消息
SendResp(resp model.Message)
// 发送广播消息
SendToGroup(group string, message model.Message)
// 发送同步广播消息
SendToGroupSync(group string, message model.Message, timeout time.Duration) error
|
channel 包
socket 包
- socket 部分则实现了socket 类型的上下文通信,主要用于非本地通信。
socket 部分主要用于远程信息交换,底层通过 net.conn 获取连接。它主要有以下几个部分组成:
- broker: 网络代理
- config: 配置
- socket: socket module
- stroe: 通信存储
- keeper: 心跳保持
- wapper: 消息打包
context_socket.go
Core.go
启动所有的module
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
// Run starts the modules and in the end does module cleanup
func Run() {
// Address the module registration and start the core
StartModules()
// monitor system signal and shutdown gracefully
GracefulShutdown()
}
|
Module.go
实现下面 4个方法,可以继承 module
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
// Module interface
type Module interface {
Name() string
Group() string
Start()
Enable() bool
}
|
message 信件
module 邮件箱
channel socket 两种交流方式,一种放完就走,一种在等待你的回复。

参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/All_Dream_and_you/article/details/128317305?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
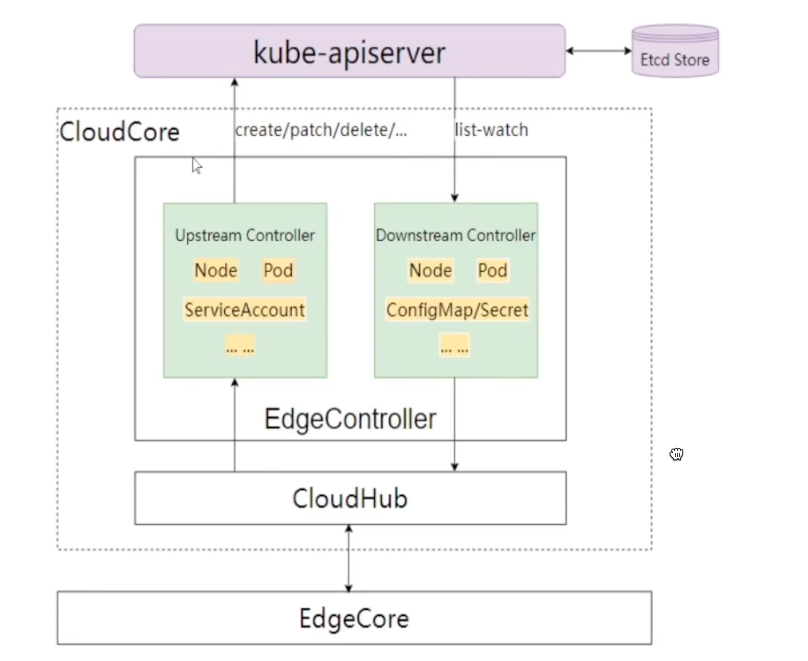
CloudCore
当 cloudcore 启动时,会将所有的module都注册到 beehive

CloudHub

CloudHub是云端组件 CloudCore 的一个模块,负责边缘节点的接入和云边数据传输,是Controller 和边缘 EdgeCore 之间的中介。它负责分发下行消息(其内封装了 k8s 资源事件,如pod update等)到边缘节点,也负责接收边缘节点发送到状态消息并转发至对应的 controllers。CloudHub 在 KubeEdge 中的位置如下所示:

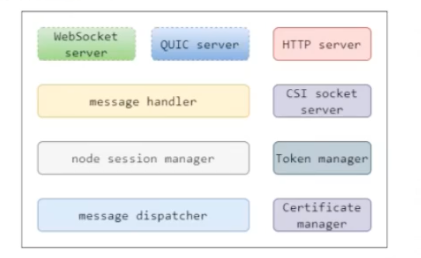
Cloudhub 内部有几个重要的代码模块,如下所示:

- HTTP server : 为边缘节点提供证书服务入口,如获取CA证书、证书签发与证书轮转
- WebSocket server: 可配置是否开启,为边缘节点提供 Websocket 协议接入服务
- QUIC server: 可配置是否开启,为边缘节点提供 QUIC 协议接入服务
- CSI socket server:在云端用来和 csi driver 通信
- Token manager: 边缘节点接入 token 凭据管理,token 默认12h 轮转
- Certificate manager :边缘节点证书签发和轮转的实现模块
- massage handler:边缘节点接入管理和边缘消息处理分发
- Node session manager: 边缘节点会话生命周期管理
- message dispatcher :上行和下行消息分发管理
CloudHub 启动流程
Cloudhub在cloud core启动时注册,通过beehive消息通信框架调用 start() 函数启动 cloudhub 模块。
1
|
cloudhub.Register(c.Modules.CloudHub)
|
CloudHub 启动的时候,首先会启动 dispatcher.DispatchDownstream 协程。用来异步分发下行消息。
其次进行证书的初始化,如果没有配置证书,则会自动生成CA和 服务证书,用于后续 websocket QUIC HTTP 服务的安全通讯。
然后启动 token manager 模块,生成边缘节点接入使用的token凭据以及开启自动轮转服务。startHTTPServer()启动服务监听,主要用于 EdgeCore 申请证书。它将等待 edgecore 发来请求,获取证书。
然后,启动Cloudhub 服务,具体的操作是使用 viaduct 中间件启动一个服务器,等待 Edgeore 发来连接请求,协议可以是基于 tcp 的WebSocket 或基于 udp 的 QUIC。如果用户需要使用 CSI 相关功能,则会启动 CSI socket server。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
func (ch *cloudHub) Start() {
// 等待同步完成
if !cache.WaitForCacheSync(beehiveContext.Done(), ch.informersSyncedFuncs...) {
klog.Errorf("unable to sync caches for objectSyncController")
os.Exit(1)
}
// start dispatch message from the cloud to edge node 分发消息到边端
go ch.dispatcher.DispatchDownstream()
// check whether the certificates exist in the local directory,
// and then check whether certificates exist in the secret, generate if they don't exist
if err := httpserver.PrepareAllCerts(); err != nil {
klog.Exit(err)
}
// TODO: Will improve in the future
DoneTLSTunnelCerts <- true
close(DoneTLSTunnelCerts)
// generate Token
if err := httpserver.GenerateToken(); err != nil {
klog.Exit(err)
}
// HttpServer mainly used to issue certificates for the edge
go httpserver.StartHTTPServer()
servers.StartCloudHub(ch.messageHandler)
if hubconfig.Config.UnixSocket.Enable {
// The uds server is only used to communicate with csi driver from kubeedge on cloud.
// It is not used to communicate between cloud and edge.
go udsserver.StartServer(hubconfig.Config.UnixSocket.Address)
}
}
|
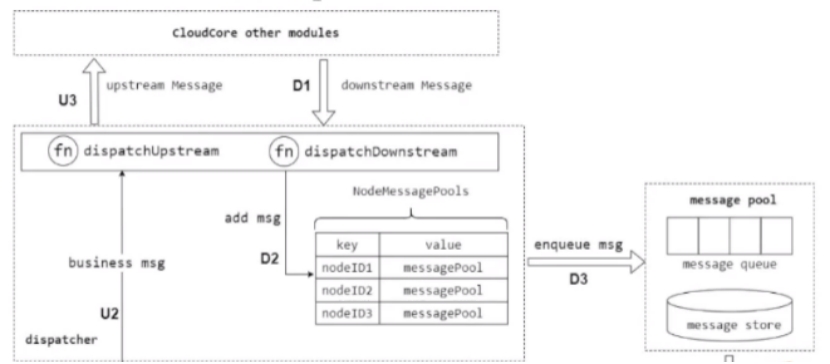
接下来,我看一下cloudhub 的核心功能,边缘节点接入管理和消息分发管理。下图是 CloudHub 的内部实现架构图:


下行消息发送模式
发送到边缘节点的下行消息,有两种发送模式,这两种发送模式,直接关系到下行消息的分发和节点session的消息处理,如下所示:
ACK模式:在这种模式下,边缘节点收到下行消息并将消息正确保存到本地数据存储之后,需要给云端发送ACK响应消息以通知消息在边缘测被正确处理,如果云端没有收到ACK消息,则认为消息没有在边缘节点正确处理,则会重试,直到收到ACK响应消息。
NO-ACK 模式:在这种模式下,边缘节点收到下行消息后,不需要给云端发送ACK响应消息,云端认为边缘测已经收到消息并正确处理,在这种模式下,消息有可能会丢失。这种模式,通常用于给边缘节点同步消息发送响应,如果边缘测没有收到响应,则会出发重试操作。
边缘节点接入
边缘节点接入的主要逻辑在messageHandler里面,handler借口如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
type Handler interface {
// HandleConnection is invoked when a new connection arrives
HandleConnection(connection conn.Connection)
// HandleMessage is invoked when a new message arrives.
HandleMessage(container *mux.MessageContainer, writer mux.ResponseWriter)
// OnEdgeNodeConnect is invoked when a new connection is established
OnEdgeNodeConnect(info *model.HubInfo, connection conn.Connection) error
// OnEdgeNodeDisconnect is invoked when a connection is lost
OnEdgeNodeDisconnect(info *model.HubInfo, connection conn.Connection)
// OnReadTransportErr is invoked when the connection read message err
OnReadTransportErr(nodeID, projectID string)
}
|
HandleConnection 用来处理边缘节点接入,以WebSocket协议接入为例,WebSocket server 通过 viaduct 启动之后,当有边缘节点接上来时,viaduct 中 serverHTTP 将 http 协议 upgrade 成为 web socket 协议,然后初始化 Connection 对象,HandleConnection 根据传入的 connection 对象进行一系列初始化操作:
-
执行初始化签前的校验工作,如是否超过配置的 node 数量限制。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
nodeID := connection.ConnectionState().Headers.Get("node_id")
projectID := connection.ConnectionState().Headers.Get("project_id")
if mh.SessionManager.ReachLimit() {
klog.Errorf("Fail to serve node %s, reach node limit", nodeID)
return
}
|
-
初始化 nodeMessagePool ,并加入到 MessageDispatcher 的哈希表中,用于存储分发的下行消息。
1
2
3
|
// init node message pool and add to the dispatcher
nodeMessagePool := common.InitNodeMessagePool(nodeID)
mh.MessageDispatcher.AddNodeMessagePool(nodeID, nodeMessagePool)
|
nodeMessagePool 是用来存储下行消息的队列,每个边缘节点的接入时,都会初始化一个对应的 nodeMessagePool,和之前的下行消息发送模式对应, nodeMessagePool 包含两个队列,分别用来存储ACK和NO-ACK模式的下行消息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
// NodeMessagePool is a collection of all downstream messages sent to an
// edge node. There are two types of messages, one that requires an ack
// and one that does not. For each type of message, we use the `queue` to
// mark the order of sending, and use the `store` to store specific messages
type NodeMessagePool struct {
// AckMessageStore store message that will send to edge node
// and require acknowledgement from edge node.
AckMessageStore cache.Store
// AckMessageQueue store message key that will send to edge node
// and require acknowledgement from edge node.
AckMessageQueue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface
// NoAckMessageStore store message that will send to edge node
// and do not require acknowledgement from edge node.
NoAckMessageStore cache.Store
// NoAckMessageQueue store message key that will send to edge node
// and do not require acknowledgement from edge node.
NoAckMessageQueue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface
}
|
-
初始化nodeSession 对象,加入到 SessionManager 哈希表中,并启动nodeSession
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
// create a node session for each edge node
nodeSession := session.NewNodeSession(nodeID, projectID, connection,
keepaliveInterval, nodeMessagePool, mh.reliableClient)
// add node session to the session manager
mh.SessionManager.AddSession(nodeSession)
// start session for each edge node and it will keep running until
// it encounters some Transport Error from underlying connection.
nodeSession.Start()
|
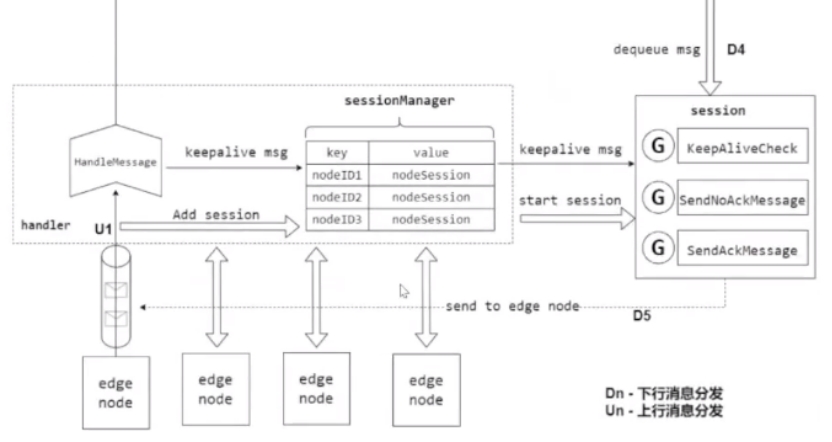
每个边缘节点对应一个nodeSession,nodeSession是对每个边缘节点连接会话的抽象,SessionManager 存储并管理连接到当前 cloudHub 的所有边缘节点的session,nodeSession启东时,会启动该节点所需要的所有处理协程。包括: KeepAliveCheck 心跳检测,SendAcKMessage 发送ACK模式的下行消息,SendNoAcKMessage 发送NO-ACK模式的下行消息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
// Start the main goroutine responsible for serving node session
func (ns *NodeSession) Start() {
klog.Infof("Start session for edge node %s", ns.nodeID)
go ns.KeepAliveCheck()
go ns.SendAckMessage()
go ns.SendNoAckMessage()
<-ns.ctx.Done()
}
|
上下行消息分发
在 CloudHub 中,上行消息的处理比较简单,主要逻辑在 Message Handler的handleMessage方法中,底层的 viaduct库进行数据的解析转换成MessageContainer对象,里面包含了message 信息,handleMessage 收到message后,进行简单的校验,然后调用 Message Dispatcher DispatcherUpstream 方法,转发到不同的模块,如 edgeController deviceController等。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
// HandleMessage handle all the request from node
func (mh *messageHandler) HandleMessage(container *mux.MessageContainer, writer mux.ResponseWriter) {
nodeID := container.Header.Get("node_id")
projectID := container.Header.Get("project_id")
// validate message
if container.Message == nil {
klog.Errorf("The message is nil for node: %s", nodeID)
return
}
klog.V(4).Infof("[messageHandler]get msg from node(%s): %+v", nodeID, container.Message)
// dispatch upstream message
mh.MessageDispatcher.DispatchUpstream(container.Message, &model.HubInfo{ProjectID: projectID, NodeID: nodeID})
}
|
下行消息的分发流程如上图D1-D5所示,以发送ACK消息为例,主要包括以下流程:
- KubeEdge使用 k8s objectSync CRD 存储已成功发送到Edge的资源的最新resourceVersion ,当CloudHub重新启动或正常启动时。它将检查待发送的资源 resourceVersion 和 已发送成功的 resourceVersion,以避免发送旧消息。
- EdgeController 和 device controller 等将消息发送到 Cloudhub ,MessageDispatcher 将根据消息中的节点名称,将消息发送到相应的 NodeMessagePool ,同时会根据消息的resource等信息来选择发送模式。在加入队列的过程中,会查询资源对应的objectSync CR ,获取发送成功的最新资源resourceVersion ,并和待加入队列的消息比较,避免重复发送。
- 节点对应的 nodeSession SendAckMessage 协程江顺序地江数据从NodeMessagePool 取出发送到相应的边缘节点。同时并将消息ID存储在 ACK channel 中,当收到来自边缘节点的ACK消息时,ACK channel 将收到通知,并将当前消息的 resourceVersion 保存到 objectSync CR 中,并发送下一条消息。
- 当Edgecore 收到消息时,它首先将消息保存到本地数据存储中,然后将ACK消息返回云端。如果cloudhub 在此间隔内未收到ACK 消息,它将继续重发该消息5次,如果所有5次重试均失败,cloudhub 将丢弃该事件。
- CloudCore 中另一个模块 SyncController 将处理这些失败的事件,即使边缘节点接收到消息,返回到ACK消息也可能在传输过程中丢失,在这种情况下,SyncController 将再次发送消息给 cloudhub ,再次触发下行消息分发,直至成功。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
func (ns *NodeSession) sendMessageWithRetry(copyMsg, msg *beehivemodel.Message) error {
ackChan := make(chan struct{})
ns.ackMessageCache.Store(copyMsg.GetID(), ackChan)
// initialize retry count and timer for sending message
retryCount := 0
ticker := time.NewTimer(sendRetryInterval)
err := ns.connection.WriteMessageAsync(copyMsg)
if err != nil {
return err
}
for {
select {
case <-ackChan:
ns.saveSuccessPoint(msg)
return nil
case <-ticker.C:
if retryCount == 4 {
return ErrWaitTimeout
}
err := ns.connection.WriteMessageAsync(copyMsg)
if err != nil {
return err
}
retryCount++
ticker.Reset(sendRetryInterval)
}
}
}
|
SyncController
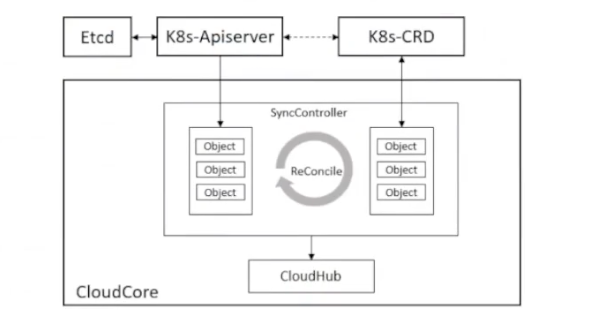
在边缘计算场景下,边缘的网络通常是不稳定的,这将导致云边的网络连接频繁断开,在云边协同通信时存在丢失数据的风险。sync controller 是 cloudCore 中的一个模块,用来保障消息的可靠性发送,在KubeEdge中,使用objectSync 对象来持久化云边协同消息状态。在云和边缘状态同步的过程中,云端会实时记录每个边缘节点同步成功的最新消息版本号(ResourceVersion)并以CR的形式持久化保存到k8s中,该机制可以保证在边缘场景下云端故障或者边缘离线重启后消息发送的顺序和连续性,避免重发旧消息引起云边状态不一致问题。与此同时,synccontroller 会周期性检查同步云边数据,保持一致性。它主要负责周期性检查各个边缘节点的同步状态,对比 k8s 中资源的信息,将不一致的状态同步到边缘,确保云边状态的最终一致性。
synccontroller 在 cloudCore 启动时注册,通过 beehive 消息通信框架调用 start()函数启动 synccontroller 模块。
1
|
synccontroller.Register(c.Modules.SyncController)
|
synccontroller 启动时,会开启周期性的检测,间隔5s执行一次
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
// Start controller
func (sctl *SyncController) Start() {
if !cache.WaitForCacheSync(beehiveContext.Done(), sctl.informersSyncedFuncs...) {
klog.Errorf("unable to sync caches for sync controller")
return
}
sctl.deleteObjectSyncs() //check outdate sync before start to reconcile
sctl.deleteClusterObjectSyncs()
go wait.Until(sctl.reconcileObjectSyncs, 5*time.Second, beehiveContext.Done())
go wait.Until(sctl.reconcileClusterObjectSyncs, 5*time.Second, beehiveContext.Done())
}
|
ObjectSync用于保存命名空间的对象,它们的名称由相关节点名称和对象UUID组成。SyncController 将定期比较保存的 ObjectSync 对象中的已发送resourceVersion 和 k8s 中的对象,然后触发诸如重试和删除之类的事件。当 cloudhub 将事件添加到 NodeMessagePool 中的相应对象进行比较。如果 NodeMessagePool 中的对象比较新,它将直接丢弃这些事件,否则CloudHub 将消息发送到边缘侧。

EdgeHub
EdgeHub 是一个Web Socket 或者 QUIC 协议的客户端,负责与云端的CloudCore 交互,包括同步云端资源更新,报告边缘主机和设备状态变化到云端等功能。
EdgeHub 在 Edgeore 启动时通过 beehive 框架注册,并对 edgehub 进行了初始化
1
2
3
4
5
|
// Register register edgehub
func Register(eh *v1alpha2.EdgeHub, nodeName string) {
config.InitConfigure(eh, nodeName)
core.Register(newEdgeHub(eh.Enable))
}
|
EdgeHub 启动代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
// Start sets context and starts the controller
func (eh *EdgeHub) Start() {
eh.certManager = certificate.NewCertManager(config.Config.EdgeHub, config.Config.NodeName)
eh.certManager.Start()
for _, v := range GetCertSyncChannel() {
v <- true
close(v)
}
go eh.ifRotationDone()
for {
select {
case <-beehiveContext.Done():
klog.Warning("EdgeHub stop")
return
default:
}
err := eh.initial()
if err != nil {
klog.Exitf("failed to init controller: %v", err)
return
}
waitTime := time.Duration(config.Config.Heartbeat) * time.Second * 2
err = eh.chClient.Init()
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("connection failed: %v, will reconnect after %s", err, waitTime.String())
time.Sleep(waitTime)
continue
}
// execute hook func after connect
eh.pubConnectInfo(true)
go eh.routeToEdge()
go eh.routeToCloud()
go eh.keepalive()
// wait the stop signal
// stop authinfo manager/websocket connection
<-eh.reconnectChan
eh.chClient.UnInit()
// execute hook fun after disconnect
eh.pubConnectInfo(false)
// sleep one period of heartbeat, then try to connect cloud hub again
klog.Warningf("connection is broken, will reconnect after %s", waitTime.String())
time.Sleep(waitTime)
// clean channel
clean:
for {
select {
case <-eh.reconnectChan:
default:
break clean
}
}
}
}
|
EdgeHub 的启动过程如下所示,主要包含以下步骤:
- 证书初始化,从 Cloudcore 申请证书(若正确配置本地证书,则直接使用本地证书),启动证书轮转模块,然后进入循环
- 调用 eh.initial() 创建 eh.chClient,接着调用 eh.chClient.init(),初始化过程通过viaduct 库建立了websoket/quic 的connection
- 调用 eh.pubConnetinfo(true),向 edge core 各模块广播已经连接成功的消息
- 接下来启动了三个协程:
- routeToEdge
- routeToCloud
- keepalive
routeToEdge:接收云端发送下来的消息,如果是同步消息响应,则调用beehive sendResp 发送响应,否则,根据消息的group,发送到对应的group
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
func (eh *EdgeHub) routeToEdge() {
for {
select {
case <-beehiveContext.Done():
klog.Warning("EdgeHub RouteToEdge stop")
return
default:
}
message, err := eh.chClient.Receive()
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("websocket read error: %v", err)
eh.reconnectChan <- struct{}{}
return
}
klog.V(4).Infof("[edgehub/routeToEdge] receive msg from cloud, msg:% +v", message)
err = eh.dispatch(message)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("failed to dispatch message, discard: %v", err)
}
}
}
|
routeToCloud 接收边缘侧其他module 发送过来的消息,然后将消息通过 web socket/quic client 发送到云端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
func (eh *EdgeHub) routeToCloud() {
for {
select {
case <-beehiveContext.Done():
klog.Warning("EdgeHub RouteToCloud stop")
return
default:
}
message, err := beehiveContext.Receive(modules.EdgeHubModuleName)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("failed to receive message from edge: %v", err)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
err = eh.tryThrottle(message.GetID())
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("msgID: %s, client rate limiter returned an error: %v ", message.GetID(), err)
continue
}
// post message to cloud hub
err = eh.sendToCloud(message)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("failed to send message to cloud: %v", err)
eh.reconnectChan <- struct{}{}
return
}
}
}
|
Keepalive:根据心跳周期定期向云端发送心跳信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
func (eh *EdgeHub) keepalive() {
for {
select {
case <-beehiveContext.Done():
klog.Warning("EdgeHub KeepAlive stop")
return
default:
}
msg := model.NewMessage("").
BuildRouter(modules.EdgeHubModuleName, "resource", "node", messagepkg.OperationKeepalive).
FillBody("ping")
// post message to cloud hub
err := eh.sendToCloud(*msg)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("websocket write error: %v", err)
eh.reconnectChan <- struct{}{}
return
}
time.Sleep(time.Duration(config.Config.Heartbeat) * time.Second)
}
}
|
- 当云边消息传送过程中出现错误时,边缘部分会重新 init 相应的 websocket/quic client ,与云端重新建立连接。
节点分组、CloudStream/EdgeStream 模块
节点分组
功能说明
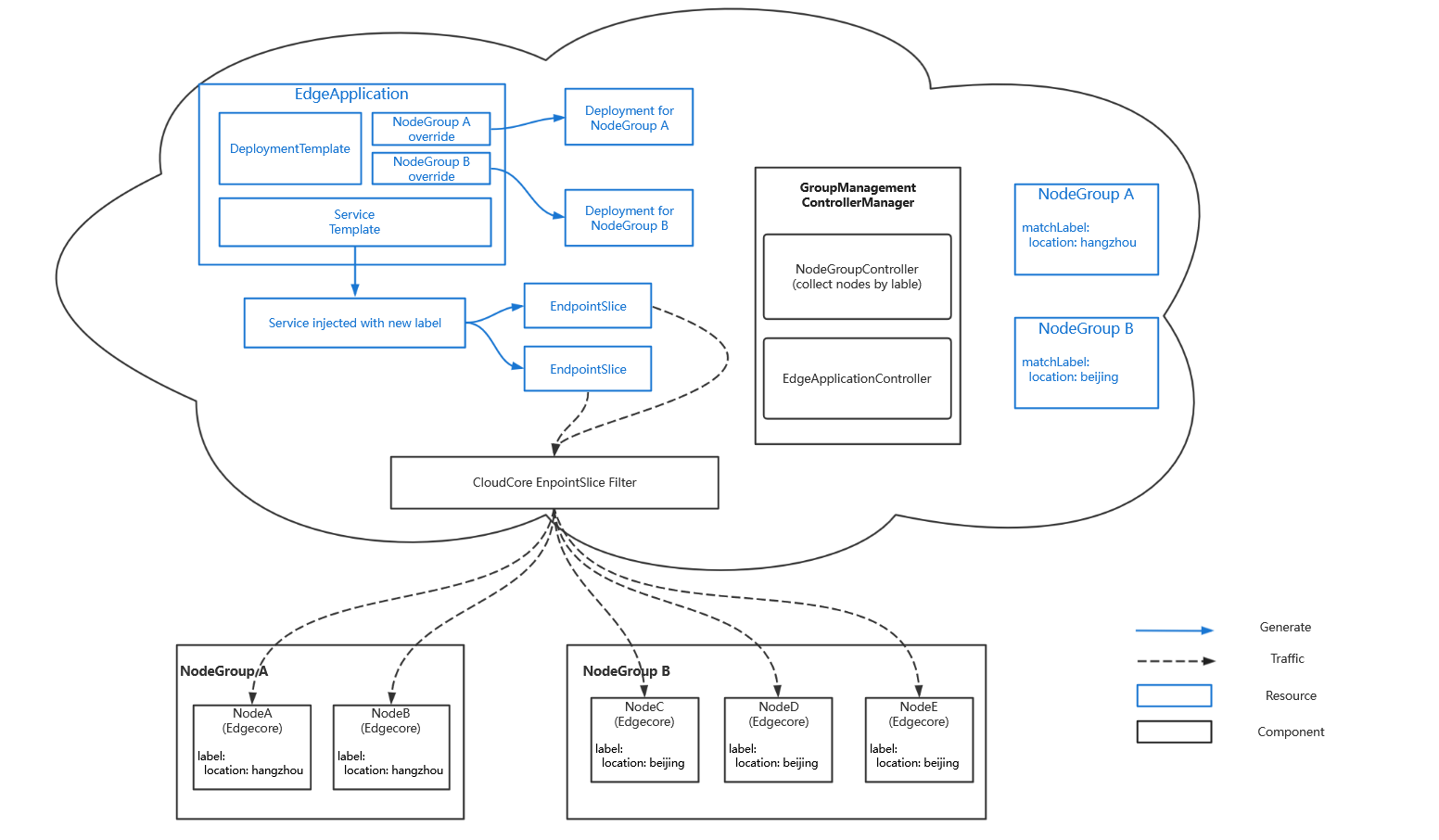
Kubeedge 1.11版本提供了”边缘节点分组管理“新特性,抽象出了跨地域的应用部署模型。该模型将边缘节点按地区划分为节点组。将服务流量限制在同一节点组中,并将应用所需资源打包成一个整体在节点组上进行部署,降低了边缘应用生命周期管理的复杂度、有效减少运维成本。
该特性由PR#3719实现
整体概览

代码路径
- NodeGroup:cloud/pkg/controllermanager/nodegroup
- EdgeApplication:cloud/pkg/controllermanager/edgeapplication
- Filter:cloud/pkg/dynamiccontroller/filter/
功能模块
NodeGroup:k8s自定义CRD,节点分组可以通过matchLabels字段,指定节点名会长节点的Label两种方式对节点进行选择,被选中的节点会被添加上apps.kubeedge.io/belonging-to:nodegroup的Label。
首先,看下NodeGroup的资源定义。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
// NodeGroup is the Schema for the nodegroups API
type NodeGroup struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
// Spec represents the specification of the desired behavior of member nodegroup.
// +required
Spec NodeGroupSpec `json:"spec,omitempty"`
// Status represents the status of member nodegroup.
// +optional
Status NodeGroupStatus `json:"status,omitempty"`
}
// NodeGroupSpec defines the desired state of NodeGroup
type NodeGroupSpec struct {
// Nodes contains names of all the nodes in the nodegroup.
// +optional
Nodes []string `json:"nodes,omitempty"`
// MatchLabels are used to select nodes that have these labels.
// +optional
MatchLabels map[string]string `json:"matchLabels,omitempty"`
}
// NodeGroupStatus contains the observed status of all selected nodes in
// this NodeGroup, including nodes that have been one of the members of this NodeGroup
// and those have not.
type NodeGroupStatus struct {
// NodeStatuses is a status list of all selected nodes.
// +optional
NodeStatuses []NodeStatus `json:"nodeStatuses,omitempty"`
}
|
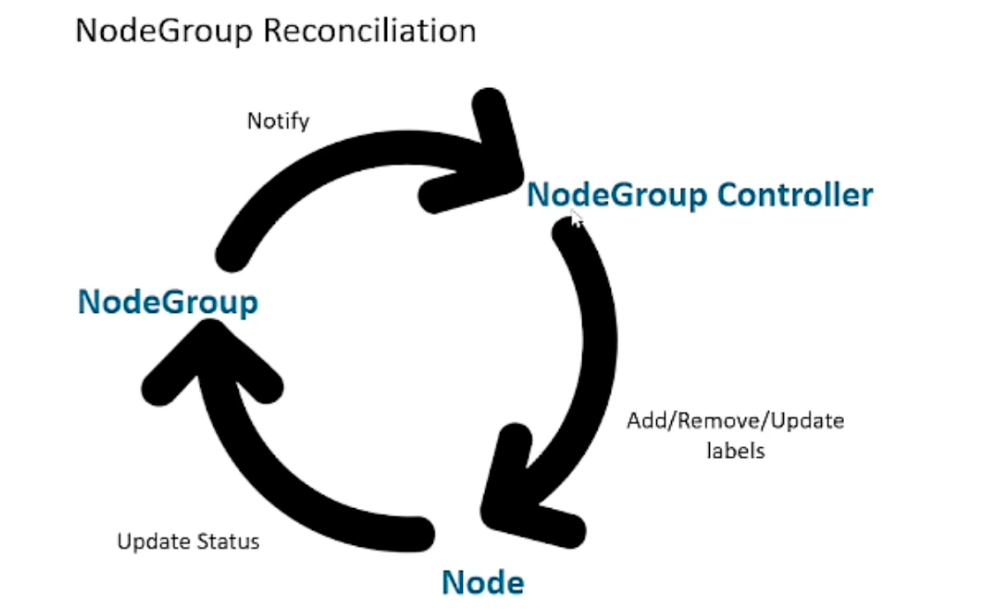
代码处理流程如下:

可以看到,NodeGroup 的处理主体流程时基于 sigs.k8s.io/controlle-runtime模块实现,通过注册nodeGroupController并启动 Reconcile 进行资源轮询,确保资源状态同步。
EdgeApplication: K8s 自定义CRD,边缘应用用于应用资源打包,按照节点组进行部署,并满足不同节点组之间的差异化部署要求。
资源定义如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
// EdgeApplication is the Schema for the edgeapplications API
type EdgeApplication struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
// Spec represents the desired behavior of EdgeApplication.
// +required
Spec EdgeApplicationSpec `json:"spec,omitempty"`
// Status represents the status of PropagationStatus.
// +optional
Status EdgeApplicationStatus `json:"status,omitempty"`
}
// EdgeApplicationSpec defines the desired state of EdgeApplication
type EdgeApplicationSpec struct {
// WorkloadTemplate contains original templates of resources to be deployed
// as an EdgeApplication.
WorkloadTemplate ResourceTemplate `json:"workloadTemplate,omitempty"`
// WorkloadScope represents which node groups the workload will be deployed in.
WorkloadScope WorkloadScope `json:"workloadScope"`
}
// WorkloadScope represents which node groups the workload should be deployed in.
type WorkloadScope struct {
// TargetNodeGroups represents the target node groups of workload to be deployed.
// +optional
TargetNodeGroups []TargetNodeGroup `json:"targetNodeGroups,omitempty"`
}
|
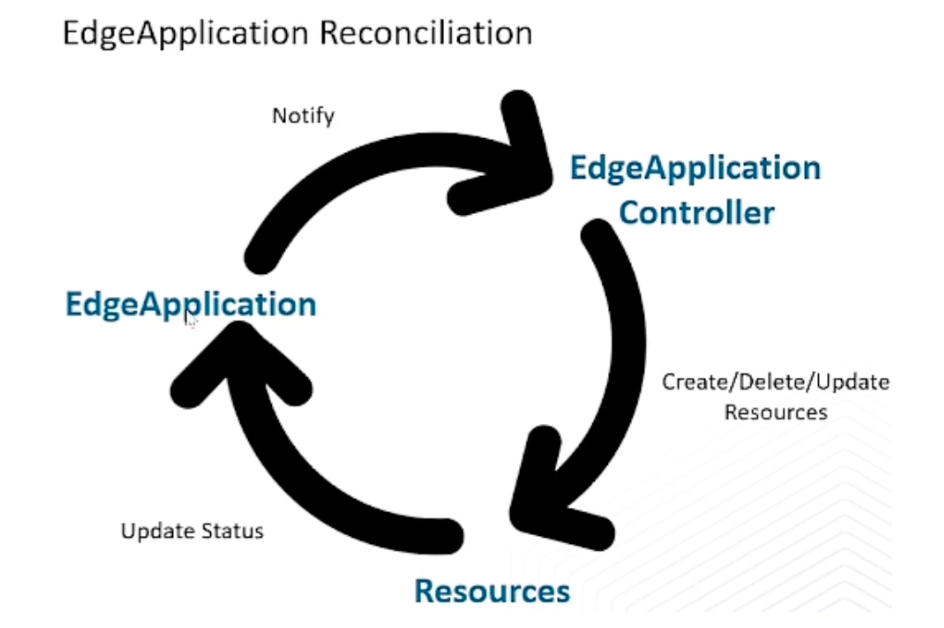
代码处理流程图如下:

EdgeApplication资源同步流程和NodeGroup类似,主体框架都是基于 于 sigs.k8s.io/controlle-runtime模块实现。
在EdgeApplication资源同步中,由两个控制器负责实现,分别是 EdgeApplication controller 和 status controller。在 EdgeApplication Controller中,主要负责子资源的更新,同步EdgeApplication资源状态和子资源状态。在 status controller 中,主要负责子资源的状态同步到EdgeApplication 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
// Reconcile performs a full reconciliation for the object referred to by the Request.
// The Controller will requeue the Request to be processed again if an error is non-nil or
// Result.Requeue is true, otherwise upon completion it will remove the work from the queue.
func (c *Controller) Reconcile(ctx context.Context, req controllerruntime.Request) (controllerruntime.Result, error) {
klog.Infof("Reconciling EdgeApplication %s/%s", req.NamespacedName.Namespace, req.NamespacedName.Name)
edgeApp := &appsv1alpha1.EdgeApplication{}
if err := c.Client.Get(ctx, req.NamespacedName, edgeApp); err != nil {
// The resource may no longer exist, in which case we stop processing.
if apierrors.IsNotFound(err) {
return controllerruntime.Result{}, nil
}
klog.Errorf("failed to get edgeapplication %s/%s, %v", req.NamespacedName.Namespace, req.NamespacedName.Name, err)
return controllerruntime.Result{Requeue: true}, err
}
if !edgeApp.DeletionTimestamp.IsZero() {
// foreground cascade deletion of OwnerReference
// will take the responsibility of removing created resources.
return controllerruntime.Result{}, nil
}
return c.syncEdgeApplication(ctx, edgeApp)
}
|
子资源状态同步:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
func (r *statusReconciler) Reconcile(ctx context.Context, request controllerruntime.Request) (controllerruntime.Result, error) {
edgeApp := &appsv1alpha1.EdgeApplication{}
if err := r.Client.Get(ctx, request.NamespacedName, edgeApp); err != nil {
if apierrors.IsNotFound(err) {
return controllerruntime.Result{}, nil
}
klog.Errorf("failed to get edgeApp %s/%s, %v", request.Namespace, request.Name, err)
return controllerruntime.Result{Requeue: true}, err
}
if !edgeApp.GetDeletionTimestamp().IsZero() {
return controllerruntime.Result{}, nil
}
return r.sync(ctx, edgeApp)
}
|
**流量闭环:**通过流量闭环的能力,将服务流量限制在同一节点组内,在一个节点组中访问service时,后端总是在同一个节点组中。当使用 EdgeApplication 中service Template 创建 service 时,会为 service 添上 service-topology:range-nodegroup 的 annotation。
kubeEdge 云上组件 CloudCore 会根据该 annotation 对 endpoint 和 endpoints slices 进行过滤,滤除不在同一节点组内的后端,之后再下发到边缘节点。
在 dynamic Controller 中,基于 K8s dynamic client 实现对 k8s 资源的 list-wath 。dynamic controller 逻辑在之前的课程中有介绍,这里重点介绍节点组流量过滤流程。
在 get/list 请求建立的短链接中,通过过滤 response 应答请求进行过滤。
过滤的资源包括 endpoint/endpointslice (后文统一以 endpoint代替),如果 endpoint 所属的 service 包含 annotation apps.kubeedge.io/service.topology:range-nodegroup ,则说明该资源需要过滤下发,根据 endpoint 关联的后端 pod 实例与目的节点是否属于同一个节点组,如果是,则下发,在下发的 endpoint中,只包含属于该节点的 pod IP 地址。最后的结果就是,节点组中的节点 listwath 到的endpoint 数据中只包含属于该节点组的 pod IP 地址,从而实现在该节点组中访问对应服务,流量只会转发到当前节点组中,从而避免跨节点组网络不通导致访问异常问题。
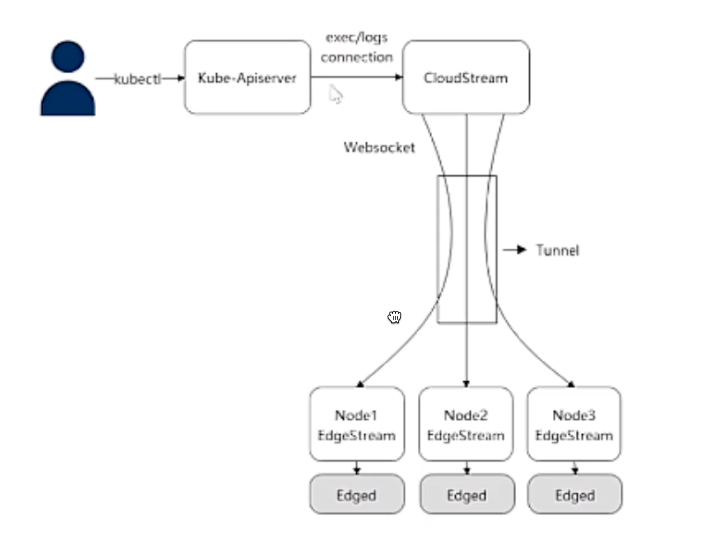
Cloudstream/Edgestream 模块解读
功能说明
Cloudstream/Edgestream 实现边缘容器的运维功能,通过在云端和边缘节点同时开启 Cloudstream/Edgestream模块,实现logs/exec/metrics/stats能力
整体概览

代码路径
- CloudStream:cloud/pkg/cloudstream
- EdgeStream:edge/pkg/edgestream
- 公共代码:pkg/stream
CloudStream流程
启动 Tunnel Server
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
func (s *TunnelServer) Start() {
s.installDefaultHandler()
var data []byte
var key []byte
var cert []byte
if streamconfig.Config.Ca != nil {
data = streamconfig.Config.Ca
klog.Info("Succeed in loading TunnelCA from local directory")
} else {
data = hubconfig.Config.Ca
klog.Info("Succeed in loading TunnelCA from CloudHub")
}
pool := x509.NewCertPool()
pool.AppendCertsFromPEM(pem.EncodeToMemory(&pem.Block{Type: certutil.CertificateBlockType, Bytes: data}))
if streamconfig.Config.Key != nil && streamconfig.Config.Cert != nil {
cert = streamconfig.Config.Cert
key = streamconfig.Config.Key
klog.Info("Succeed in loading TunnelCert and Key from local directory")
} else {
cert = hubconfig.Config.Cert
key = hubconfig.Config.Key
klog.Info("Succeed in loading TunnelCert and Key from CloudHub")
}
certificate, err := tls.X509KeyPair(pem.EncodeToMemory(&pem.Block{Type: certutil.CertificateBlockType, Bytes: cert}), pem.EncodeToMemory(&pem.Block{Type: "PRIVATE KEY", Bytes: key}))
if err != nil {
klog.Error("Failed to load TLSTunnelCert and Key")
panic(err)
}
tunnelServer := &http.Server{
Addr: fmt.Sprintf(":%d", streamconfig.Config.TunnelPort),
Handler: s.container,
TLSConfig: &tls.Config{
ClientCAs: pool,
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{certificate},
ClientAuth: tls.RequireAndVerifyClientCert,
MinVersion: tls.VersionTLS12,
CipherSuites: []uint16{tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256},
},
}
klog.Infof("Prepare to start tunnel server ...")
err = tunnelServer.ListenAndServeTLS("", "")
if err != nil {
klog.Exitf("Start tunnelServer error %v\n", err)
return
}
}
|
EdgeStream 流程
EdgeStream 模块启动后,连接云上 CloudStream。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
func (e *edgestream) Start() {
serverURL := url.URL{
Scheme: "wss",
Host: config.Config.TunnelServer,
Path: "/v1/kubeedge/connect",
}
// TODO: Will improve in the future
if ok := <-edgehub.GetCertSyncChannel()[e.Name()]; !ok {
klog.Exitf("Failed to find cert key pair")
}
cert, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair(config.Config.TLSTunnelCertFile, config.Config.TLSTunnelPrivateKeyFile)
if err != nil {
klog.Exitf("Failed to load x509 key pair: %v", err)
}
tlsConfig := &tls.Config{
InsecureSkipVerify: true,
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{cert},
}
ticker := time.NewTicker(time.Second * 2)
defer ticker.Stop()
for {
select {
case <-beehiveContext.Done():
return
case <-ticker.C:
err := e.TLSClientConnect(serverURL, tlsConfig)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("TLSClientConnect error %v", err)
}
}
}
}
|
节点与应用生命周期管理源码解析
EdgeController
EdgeController 是 Kubernetes API server和 EdgeCore 之间的桥梁,负责节点管理和应用状态数据云边协同。EdgeController映射的是一组核心 API 在云 和 边缘状态的同步,在实现上使用了两个内部 controller ,分别是处理上行消息 Upstream Controller和处理下行消息的 Downstream Controller

EdgeController模块注册与启动
EdgeController在 CloudCore 启动时发起注册,同样使用 beehive 框架注册 EdgeController 模块。
1
|
core.Register(newEdgeController(ec))
|
EdgeController 的启动主要包括两个 controller 的启动,即上行消息控制器 Upstream Controller 和 下行消息控制器 Downstream controller 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
// Start controller
func (ec *EdgeController) Start() {
if err := ec.upstream.Start(); err != nil {
klog.Exitf("start upstream failed with error: %s", err)
}
if err := ec.downstream.Start(); err != nil {
klog.Exitf("start downstream failed with error: %s", err)
}
}
|
下面依次查看两个消息控制器的启动与消息处理流程。
Upstream Controller
上行消息主要指边缘 Edged向集群master发送的消息,主要包括 Edged 启动时注册node的消息,边缘上报的 nodestatus 与 podstatus 以及边缘发起的请求消息,譬如query secret 和 configmap 等。Upstream Controller 工作流程就是接收 cloud hub 发送的消息,根据不同的消息类型,对应地通过 kubeclient 访问 k8s 集群处理消息,并返回 response到边缘。
- Upstream 的创建与结构
首先可以看下 Upstream 的结构定义,主要包括:
- KubeClient,用于访问 api-server,上报消息到k8s 集群或者 获取资源。
- messageLayer,用于分发消息,主要包括Send/Receive/Response方法。
- crdClient,在updateRuleStatus时用来更新crd。
- 消息 channel,各种类型的消息channel
- lister,为各种消息资源创建的lister方法,用于处理对应消息的query请求。
代码路径:cloud/pkg/edgecontroller/controller/upstream.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
// UpstreamController subscribe messages from edge and sync to k8s api server
type UpstreamController struct {
kubeClient kubernetes.Interface
messageLayer messagelayer.MessageLayer
crdClient crdClientset.Interface
config v1alpha1.EdgeController
// message channel
nodeStatusChan chan model.Message
podStatusChan chan model.Message
secretChan chan model.Message
serviceAccountTokenChan chan model.Message
configMapChan chan model.Message
persistentVolumeChan chan model.Message
persistentVolumeClaimChan chan model.Message
volumeAttachmentChan chan model.Message
queryNodeChan chan model.Message
createNodeChan chan model.Message
patchNodeChan chan model.Message
updateNodeChan chan model.Message
patchPodChan chan model.Message
podDeleteChan chan model.Message
ruleStatusChan chan model.Message
createLeaseChan chan model.Message
queryLeaseChan chan model.Message
createPodChan chan model.Message
// lister
podLister corelisters.PodLister
configMapLister corelisters.ConfigMapLister
secretLister corelisters.SecretLister
nodeLister corelisters.NodeLister
leaseLister coordinationlisters.LeaseLister
}
|
- Upstream 启动
Upstream 的启动过程主要由启动消息分发协程和启动各个消息处理协程组成。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
// Start UpstreamController
func (uc *UpstreamController) Start() error {
klog.Info("start upstream controller")
go uc.dispatchMessage()
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.UpdateNodeStatusWorkers); i++ {
go uc.updateNodeStatus()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.UpdatePodStatusWorkers); i++ {
go uc.updatePodStatus()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.QueryConfigMapWorkers); i++ {
go uc.queryConfigMap()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.QuerySecretWorkers); i++ {
go uc.querySecret()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.ServiceAccountTokenWorkers); i++ {
go uc.processServiceAccountToken()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.QueryPersistentVolumeWorkers); i++ {
go uc.queryPersistentVolume()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.QueryPersistentVolumeClaimWorkers); i++ {
go uc.queryPersistentVolumeClaim()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.QueryVolumeAttachmentWorkers); i++ {
go uc.queryVolumeAttachment()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.CreateNodeWorkers); i++ {
go uc.registerNode()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.PatchNodeWorkers); i++ {
go uc.patchNode()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.QueryNodeWorkers); i++ {
go uc.queryNode()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.UpdateNodeWorkers); i++ {
go uc.updateNode()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.PatchPodWorkers); i++ {
go uc.patchPod()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.DeletePodWorkers); i++ {
go uc.deletePod()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.CreateLeaseWorkers); i++ {
go uc.createOrUpdateLease()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.QueryLeaseWorkers); i++ {
go uc.queryLease()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.UpdateRuleStatusWorkers); i++ {
go uc.updateRuleStatus()
}
for i := 0; i < int(uc.config.Load.CreatePodWorks); i++ {
go uc.createPod()
}
return nil
}
|
- 消息分发
消息分发操作步骤:
- 由messageLayer的Receiver的方法接收上行消息(边缘通过cloudhub分发到edgecontroller的消息)
- 解析消息,获取消息的具体类型
- 根据消息类型,写入到对应的消息channel中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
|
func (uc *UpstreamController) dispatchMessage() {
for {
select {
case <-beehiveContext.Done():
klog.Info("stop dispatchMessage")
return
default:
}
msg, err := uc.messageLayer.Receive()
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("receive message failed, %s", err)
continue
}
klog.V(5).Infof("dispatch message ID: %s", msg.GetID())
klog.V(5).Infof("dispatch message content: %+v", msg)
resourceType, err := messagelayer.GetResourceType(msg)
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("parse message: %s resource type with error, message resource: %s, err: %v", msg.GetID(), msg.GetResource(), err)
continue
}
klog.V(5).Infof("message: %s, operation type is: %s", msg.GetID(), msg.GetOperation())
switch resourceType {
case model.ResourceTypeNodeStatus:
uc.nodeStatusChan <- msg
case model.ResourceTypePodStatus:
uc.podStatusChan <- msg
case model.ResourceTypeConfigmap:
uc.configMapChan <- msg
case model.ResourceTypeSecret:
uc.secretChan <- msg
case model.ResourceTypeServiceAccountToken:
uc.serviceAccountTokenChan <- msg
case common.ResourceTypePersistentVolume:
uc.persistentVolumeChan <- msg
case common.ResourceTypePersistentVolumeClaim:
uc.persistentVolumeClaimChan <- msg
case common.ResourceTypeVolumeAttachment:
uc.volumeAttachmentChan <- msg
case model.ResourceTypeNode:
switch msg.GetOperation() {
case model.InsertOperation:
uc.createNodeChan <- msg
case model.QueryOperation:
uc.queryNodeChan <- msg
case model.UpdateOperation:
uc.updateNodeChan <- msg
default:
klog.Errorf("message: %s, operation type: %s unsupported", msg.GetID(), msg.GetOperation())
}
case model.ResourceTypeNodePatch:
uc.patchNodeChan <- msg
case model.ResourceTypePodPatch:
uc.patchPodChan <- msg
case model.ResourceTypePod:
switch msg.GetOperation() {
case model.DeleteOperation:
uc.podDeleteChan <- msg
case model.InsertOperation:
uc.createPodChan <- msg
default:
klog.Errorf("message: %s, operation type: %s unsupported", msg.GetID(), msg.GetOperation())
}
case model.ResourceTypeRuleStatus:
uc.ruleStatusChan <- msg
case model.ResourceTypeLease:
switch msg.GetOperation() {
case model.InsertOperation, model.UpdateOperation:
uc.createLeaseChan <- msg
case model.QueryOperation:
uc.queryLeaseChan <- msg
}
default:
klog.Errorf("message: %s, resource type: %s unsupported", msg.GetID(), resourceType)
}
}
}
|
- 消息处理
edgecontroller目前支持处理的消息类型包括:
- registerNode(注册节点)/patchNode(更新Node)/queryNode(查询Node)/updateNodeStatus(更新node状态,V1.12之后已废弃)/updateNode(更新node,v1.12之后已废弃)
- createOrUpdateLease(创建或更新node lease)/ queryLease (查询node lease)
- patchPod (更新pod)/ deletePod (删除pod)/updatePodStatus(更新pod状态,v1.12之后已废弃)
- processServiceAccouToken (获取serviceAccountToken)
- queryXXX (获取configMap/Secret等资源)
- updateRuleStatus(更新规则状态)
本文以 patchNode 为例,详细介绍处理对应消息的流程,其他消息类型都与之类似。
消息处理步骤:
- 起一个 for 循环,等待 patchNodeChan 里的消息,当dispatchMessage 函数写入到该channel,开始处理消息。
- 解析消息,获得namespace和node name
- 获取消息的内容,即边缘上报的patch内容
- 使用kubeclient直接调用patch方法更新node
- 将patchNode返回的response和error都塞入response的消息体内,调用messageLayer的Respose方法直接透传回边缘。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
func (uc *UpstreamController) patchNode() {
for {
select {
case <-beehiveContext.Done():
klog.Warning("stop patchNode")
return
case msg := <-uc.patchNodeChan:
klog.V(5).Infof("message: %s, operation is: %s, and resource is %s", msg.GetID(), msg.GetOperation(), msg.GetResource())
namespace, err := messagelayer.GetNamespace(msg)
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("message: %s process failure, get namespace failed with error: %v", msg.GetID(), err)
continue
}
name, err := messagelayer.GetResourceName(msg)
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("message: %s process failure, get resource name failed with error: %v", msg.GetID(), err)
continue
}
// 直接用 patch 方法更新 k8s 中的节点
patchBytes, err := msg.GetContentData()
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("message: %s process failure, get data failed with error: %v", msg.GetID(), err)
continue
}
// 直接把 k8s 的response 透传回边缘
node, err := uc.kubeClient.CoreV1().Nodes().Patch(context.TODO(), name, apimachineryType.StrategicMergePatchType, patchBytes, metaV1.PatchOptions{}, "status")
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("message: %s process failure, patch node failed with error: %v, namespace: %s, name: %s", msg.GetID(), err, namespace, name)
}
resMsg := model.NewMessage(msg.GetID()).
SetResourceVersion(node.ResourceVersion).
FillBody(&edgeapi.ObjectResp{Object: node, Err: err}).
BuildRouter(modules.EdgeControllerModuleName, constants.GroupResource, msg.GetResource(), model.ResponseOperation)
if err = uc.messageLayer.Response(*resMsg); err != nil {
klog.Warningf("Message: %s process failure, response failed with error: %v", msg.GetID(), err)
continue
}
klog.V(4).Infof("message: %s, patch node status successfully, namespace: %s, name: %s", msg.GetID(), namespace, name)
}
}
}
|
Downstream Controller
下行消息控制器主要用于监听 k8s 事件,同步消息到边缘。在原生的k8s中,节点是直接通过list-watch来监听事件,并更新节点资源的。但是在负责的边缘场景中,边缘并不是直接通过HTTP访问云上,在 KubeEdge 中,云边协同是通过 websocket 进行通信的,所以就需要在云上通过 DownStream Controller 通过list-watch来监听实践,并且把更新的元数据同步到边缘。
Downstream 的结构主要包括:
- kubeclient ,用于访问k8s 集群
- messageLayer ,分发消息
- podManager 等,各个资源的管理器,主要用于监听对应资源的事件,在第二部分详细展开介绍。
- lc,本地缓存,由多个map结构组成,key为各种资源类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
// DownstreamController watch kubernetes api server and send change to edge
type DownstreamController struct {
kubeClient kubernetes.Interface
messageLayer messagelayer.MessageLayer
podManager *manager.PodManager
configmapManager *manager.ConfigMapManager
secretManager *manager.SecretManager
nodeManager *manager.NodesManager
rulesManager *manager.RuleManager
ruleEndpointsManager *manager.RuleEndpointManager
lc *manager.LocationCache
podLister clientgov1.PodLister
}
|
DownStream 的创建过程主要包括各个资源管理器的创建以及本地缓存的初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
// NewDownstreamController create a DownstreamController from config
func NewDownstreamController(config *v1alpha1.EdgeController, k8sInformerFactory k8sinformers.SharedInformerFactory, keInformerFactory informers.KubeEdgeCustomInformer,
crdInformerFactory crdinformers.SharedInformerFactory) (*DownstreamController, error) {
lc := &manager.LocationCache{}
// 创建各个资源类型对应的管理器
podInformer := k8sInformerFactory.Core().V1().Pods()
podManager, err := manager.NewPodManager(config, podInformer.Informer())
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("create pod manager failed with error: %s", err)
return nil, err
}
configMapInformer := k8sInformerFactory.Core().V1().ConfigMaps()
configMapManager, err := manager.NewConfigMapManager(config, configMapInformer.Informer())
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("create configmap manager failed with error: %s", err)
return nil, err
}
secretInformer := k8sInformerFactory.Core().V1().Secrets()
secretManager, err := manager.NewSecretManager(config, secretInformer.Informer())
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("create secret manager failed with error: %s", err)
return nil, err
}
nodeInformer := keInformerFactory.EdgeNode()
nodesManager, err := manager.NewNodesManager(nodeInformer)
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("Create nodes manager failed with error: %s", err)
return nil, err
}
rulesInformer := crdInformerFactory.Rules().V1().Rules().Informer()
rulesManager, err := manager.NewRuleManager(config, rulesInformer)
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("Create rulesManager failed with error: %s", err)
return nil, err
}
ruleEndpointsInformer := crdInformerFactory.Rules().V1().RuleEndpoints().Informer()
ruleEndpointsManager, err := manager.NewRuleEndpointManager(config, ruleEndpointsInformer)
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("Create ruleEndpointsManager failed with error: %s", err)
return nil, err
}
dc := &DownstreamController{
kubeClient: client.GetKubeClient(),
podManager: podManager,
configmapManager: configMapManager,
secretManager: secretManager,
nodeManager: nodesManager,
messageLayer: messagelayer.EdgeControllerMessageLayer(),
lc: lc,
podLister: podInformer.Lister(),
rulesManager: rulesManager,
ruleEndpointsManager: ruleEndpointsManager,
}
// 初始化缓存
if err := dc.initLocating(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return dc, nil
}
|
-
资源管理器
EdgeController 目前包括6种资源管理器,分别是PodManager、NodeManager、ConfigMapManager、SecretManager、RuleManager和RuleEndpointManager。本文以PodManager为例,详细介绍Downstream中的资源管理器。
PodManager中的主要包括两个Channel,realEvents表示从K8s watch到的实际pod事件,mergedEvents是根据KubeEdge自身需求,通过对 realEvents watch 到的事件进行预处理后再写入Channel。
注意事项:只有PodManager有两个Event Channel,其余资源的Manager都只有一个channel,用来监听K8s更新事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
// PodManager is a manager watch pod change event
type PodManager struct {
// events from watch kubernetes api server
realEvents chan watch.Event
// events merged
mergedEvents chan watch.Event
}
|
PodManager的创建包括了两个步骤,一个是运行ShareInformer,ShareInformer用于创建list-watch实例,注册事件监听,从而监听到集群中的pod的更新事件,第二步是起一个merge协程,用于对从 realEvents Channel监听到更新事件进行预处理,并写入mergeEvents Channel。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
// NewPodManager create PodManager from config
func NewPodManager(config *v1alpha1.EdgeController, si cache.SharedIndexInformer) (*PodManager, error) {
realEvents := make(chan watch.Event, config.Buffer.PodEvent)
mergedEvents := make(chan watch.Event, config.Buffer.PodEvent)
rh := NewCommonResourceEventHandler(realEvents, &podEventFilter{})
si.AddEventHandler(rh)
pm := &PodManager{realEvents: realEvents, mergedEvents: mergedEvents}
go pm.merge()
return pm, nil
}
|
- Downstream Controller 的启动
Downstream Controller 的启动即启动各个资源同步函数的协程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
// Start DownstreamController
func (dc *DownstreamController) Start() error {
klog.Info("start downstream controller")
// pod
go dc.syncPod()
// configmap
go dc.syncConfigMap()
// secret
go dc.syncSecret()
// nodes
go dc.syncEdgeNodes()
// rule
go dc.syncRule()
// ruleendpoint
go dc.syncRuleEndpoint()
return nil
}
|
- 资源同步
同样以syncPod为例,介绍一下资源同步到边缘的步骤。SyncPod函数同样起了一个for循环,始终监听PodManager中的mergedEvents Channel。
- 当有pod更新事件发生时,从Channel中读出事件
- 解析事件,从中获取新的podfd
- 根据pod中的nodename,namespace等信息,构建下行消息。
- 根据事件类型(Added/Deleted/Modified),设置下行消息的操作类型,并更新本地缓存
- 发送消息到边缘
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
func (dc *DownstreamController) syncPod() {
for {
select {
case <-beehiveContext.Done():
klog.Warning("Stop edgecontroller downstream syncPod loop")
return
// 监听到 pod 更新事件
case e := <-dc.podManager.Events():
// 解析 event 获得事件中的pod
pod, ok := e.Object.(*v1.Pod)
if !ok {
klog.Warningf("object type: %T unsupported", e.Object)
continue
}
if !dc.lc.IsEdgeNode(pod.Spec.NodeName) {
continue
}
// 构建下行消息
resource, err := messagelayer.BuildResource(pod.Spec.NodeName, pod.Namespace, model.ResourceTypePod, pod.Name)
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("built message resource failed with error: %s", err)
continue
}
msg := model.NewMessage("").
SetResourceVersion(pod.ResourceVersion).
FillBody(pod)
// 根据事件类型,设置下行消息的router,并更新缓存
switch e.Type {
case watch.Added:
msg.BuildRouter(modules.EdgeControllerModuleName, constants.GroupResource, resource, model.InsertOperation)
dc.lc.AddOrUpdatePod(*pod)
case watch.Deleted:
msg.BuildRouter(modules.EdgeControllerModuleName, constants.GroupResource, resource, model.DeleteOperation)
case watch.Modified:
msg.BuildRouter(modules.EdgeControllerModuleName, constants.GroupResource, resource, model.UpdateOperation)
dc.lc.AddOrUpdatePod(*pod)
default:
klog.Warningf("pod event type: %s unsupported", e.Type)
continue
}
// 发送消息到边缘
if err := dc.messageLayer.Send(*msg); err != nil {
klog.Warningf("send message failed with error: %s, operation: %s, resource: %s", err, msg.GetOperation(), msg.GetResource())
} else {
klog.V(4).Infof("send message successfully, operation: %s, resource: %s", msg.GetOperation(), msg.GetResource())
}
}
}
}
|
MetaManager 作为Edgehub与Edged消息交互的桥梁,不仅仅负责消息转发,更重要的是将元数据保存在边缘数据库中,当边云连接断开时,可以保障边缘业务稳定运行,尤其是当边缘节点重启时,Edged可以直接通过MetaManager从数据库读取元数据,保证边缘业务的快速恢复,达到边缘自治的能力。
本文仅介绍metaManager处理元数据的流程
metamanager启动时 会起一个处理数据的process协程,在协程中启动一个for循环,在循环中接收消息,并对消息进行处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
func (m *metaManager) runMetaManager() {
go func() {
for {
select {
case <-beehiveContext.Done():
klog.Warning("MetaManager main loop stop")
return
default:
}
// 接收消息
msg, err := beehiveContext.Receive(m.Name())
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("get a message %+v: %v", msg, err)
continue
}
klog.V(2).Infof("get a message %+v", msg)
// 处理消息
m.process(msg)
}
}()
}
|
MetaManager 会根据消息操作类型,做出对应的处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
func (m *metaManager) process(message model.Message) {
operation := message.GetOperation()
switch operation {
case model.InsertOperation:
m.processInsert(message)
case model.UpdateOperation:
m.processUpdate(message)
case model.PatchOperation:
m.processPatch(message)
case model.DeleteOperation:
m.processDelete(message)
case model.QueryOperation:
m.processQuery(message)
case model.ResponseOperation:
m.processResponse(message)
case constants.CSIOperationTypeCreateVolume,
constants.CSIOperationTypeDeleteVolume,
constants.CSIOperationTypeControllerPublishVolume,
constants.CSIOperationTypeControllerUnpublishVolume:
m.processVolume(message)
default:
klog.Errorf("metamanager not supported operation: %v", operation)
}
}
|
以Insert为例,MetaManager 接收到消息之后,会解析出消息的内容以及 resourceKey (一般为{namespace}/{restype}/{resld}结构)和type,并将其保存到边缘数据库。之后会根据消息的具体信息,包括源模块、消息类型等,将消息转发至目的模块。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
func (m *metaManager) processInsert(message model.Message) {
imitator.DefaultV2Client.Inject(message)
msgSource := message.GetSource()
if msgSource == modules.EdgedModuleName {
if !connect.IsConnected() {
klog.Warningf("process remote failed, req[%s], err: %v", msgDebugInfo(&message), errNotConnected)
feedbackError(fmt.Errorf("failed to process remote: %s", errNotConnected), message)
return
}
m.processRemote(message)
return
}
if err := m.handleMessage(&message); err != nil {
feedbackError(err, message)
return
}
if msgSource == cloudmodules.DeviceControllerModuleName {
message.SetRoute(modules.MetaGroup, modules.DeviceTwinModuleName)
beehiveContext.Send(modules.DeviceTwinModuleName, message)
} else if msgSource != cloudmodules.PolicyControllerModuleName {
// Notify edged
sendToEdged(&message, false)
}
resp := message.NewRespByMessage(&message, OK)
sendToCloud(resp)
}
|
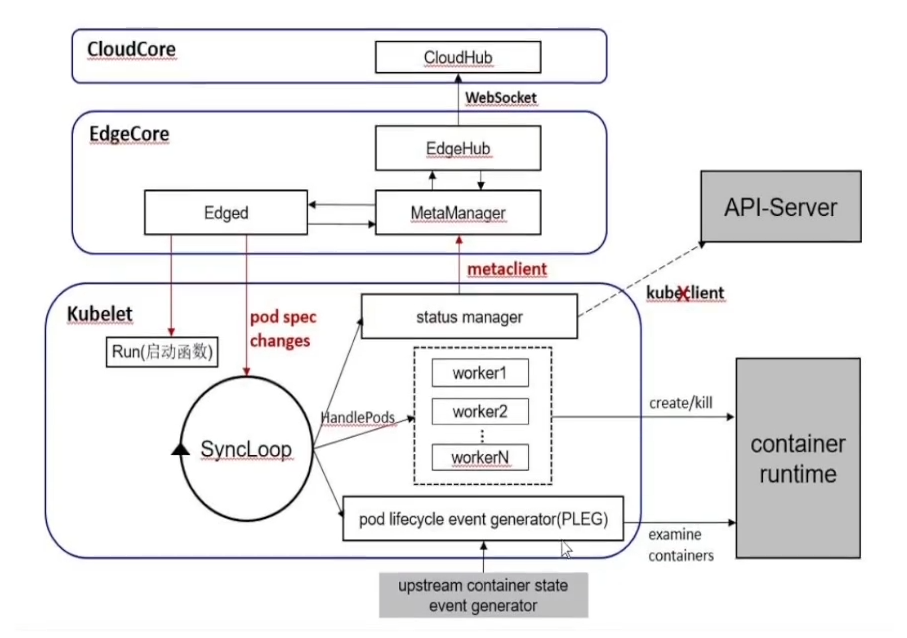
Edged
本文以新版Edged(v1.12之后)为例,新版直接在Edged中集成了裁剪之后的kubelet,所以在后面的功能模块源码解析中会涉及一部分的kubelet代码,有关kubelet源码更详细的解读还需要大家提前学习下Kubernetes。

关于Edged模块的源码解析,我们会从三个部分进行,分别是Edged的注册与启动、Edged上报消息链路和下行消息处理链路。
Edged的注册与启动
Edged 模块的注册同样是调用 beehive 框架公共方法来注册模块,这里的主要工作是完成Edged的创建。
Edged的创建主要工作包括:
- 参数的初始化,由于新版Edged直接集成kubelet,所以需要先把Edged的参数转换成kubelet启动所需的参数。Kubelet的启动涉及两类参数,KubeletConfiguration 和KubeletFlags,所以这里通过两个参数转换函数将Edged的参数转换为kubelet的启动参数。
- 调用UnsecureDependencies函数初始化一些运行时所需的参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
// newEdged creates new edged object and initialises it
func newEdged(enable bool, nodeName, namespace string) (*edged, error) {
var ed *edged
var err error
if !enable {
return &edged{
enable: enable,
nodeName: nodeName,
namespace: namespace,
}, nil
}
// initial kubelet config and flag
var kubeletConfig kubeletconfig.KubeletConfiguration
var kubeletFlags kubeletoptions.KubeletFlags
err = edgedconfig.ConvertEdgedKubeletConfigurationToConfigKubeletConfiguration(edgedconfig.Config.TailoredKubeletConfig, &edgedconfig.Config.TailoredKubeletFlag, &kubeletConfig, nil)
if err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to convert kubelet config")
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to construct kubelet configuration")
}
edgedconfig.ConvertConfigEdgedFlagToConfigKubeletFlag(&edgedconfig.Config.TailoredKubeletFlag, &kubeletFlags)
// Set Kubelet RegisterNode Parameter in KubeletConfiguration.
// The parameter `registerNode` has been migrated to Kubelet Configuration.
// `registerNode` in KubeletFlag will be retained for next version(1.13), and removed in 1.14 and later.
if !edgedconfig.Config.RegisterNode {
kubeletConfig.RegisterNode = false
}
// set feature gates from initial flags-based config
if err := utilfeature.DefaultMutableFeatureGate.SetFromMap(kubeletConfig.FeatureGates); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to set feature gates from initial flags-based config: %w", err)
}
// construct a KubeletServer from kubeletFlags and kubeletConfig
kubeletServer := kubeletoptions.KubeletServer{
KubeletFlags: kubeletFlags,
KubeletConfiguration: kubeletConfig,
}
// make directory for static pod
if kubeletConfig.StaticPodPath != "" {
if err := os.MkdirAll(kubeletConfig.StaticPodPath, os.ModePerm); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("create %s static pod path failed: %v", kubeletConfig.StaticPodPath, err)
}
} else {
klog.ErrorS(err, "static pod path is nil!")
}
// set edged version
nodestatus.KubeletVersion = fmt.Sprintf("%s-kubeedge-%s", constants.CurrentSupportK8sVersion, version.Get())
// use kubeletServer to construct the default KubeletDeps
kubeletDeps, err := DefaultKubeletDeps(&kubeletServer, utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate)
if err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to construct kubelet dependencies")
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to construct kubelet dependencies")
}
MakeKubeClientBridge(kubeletDeps)
// source of all configuration
kubeletDeps.PodConfig = config.NewPodConfig(config.PodConfigNotificationIncremental, kubeletDeps.Recorder, kubeletDeps.PodStartupLatencyTracker)
ed = &edged{
enable: true,
context: context.Background(),
KubeletServer: &kubeletServer,
KubeletDeps: kubeletDeps,
FeatureGate: utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate,
nodeName: nodeName,
namespace: namespace,
}
return ed, nil
}
|
- MakeKubeClientBridge ,新建metaClient,替换原生Kubelet里的KubeClient。原生Kubelet通过KubeClient访问apiserver上报节点消息,在KubeEdge中,通过这层替换,Kubelet会通过metaClient上报消息到 MetaManager,进而通过Websocket链路上报到云上。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
// MakeKubeClientBridge make kubeclient bridge to replace kubeclient with metaclient
func MakeKubeClientBridge(kubeletDeps *kubelet.Dependencies) {
client := kubebridge.NewSimpleClientset(metaclient.New())
kubeletDeps.KubeClient = client
kubeletDeps.EventClient = nil
kubeletDeps.HeartbeatClient = client
}
|
- NewPodConfig ,用于新建kubelet启动所需的PodConfig,用于之后下行的pod消息写入。
Edged的启动过程比较简单,直接通过调用 kubelet的启动函数即可。syncPod函数用于处理下行的Pod消息,在之后的第三部分会详细介绍。