基于 Kubernetes 的云原生 AI 平台建设
提高算力资源利用
- GPU 虚拟化
GPUManager 基于 GPU 驱动封装实现,用户需要对驱动的某些关键接口(如显存分配、cuda thread 创建等)进行封装劫持,在劫持过程中限制用户进程对计算资源的使用,整体方案较为轻量化、性能损耗小,自身只有 5% 的性能损耗,支持同一张卡上容器间 GPU 和显存使用隔离,保证了编码这种算力利用率不高的场景开发者可以共享 GPU,同时在同一块调试时资源不会被抢占。
- 训练集群算力调度
在 Kubernetes 里面使用 Job 来创建训练任务,只需要指定需要使用的GPU资源,结合消息队列,训练集群算力资源利用率可以达到满载。
- 资源监控
资源监控对集群编码、训练优化有关键指导作用,可以限制每个项目 GPU 总的使用量和每个用户GPU 资源分配。

kubeflow介绍
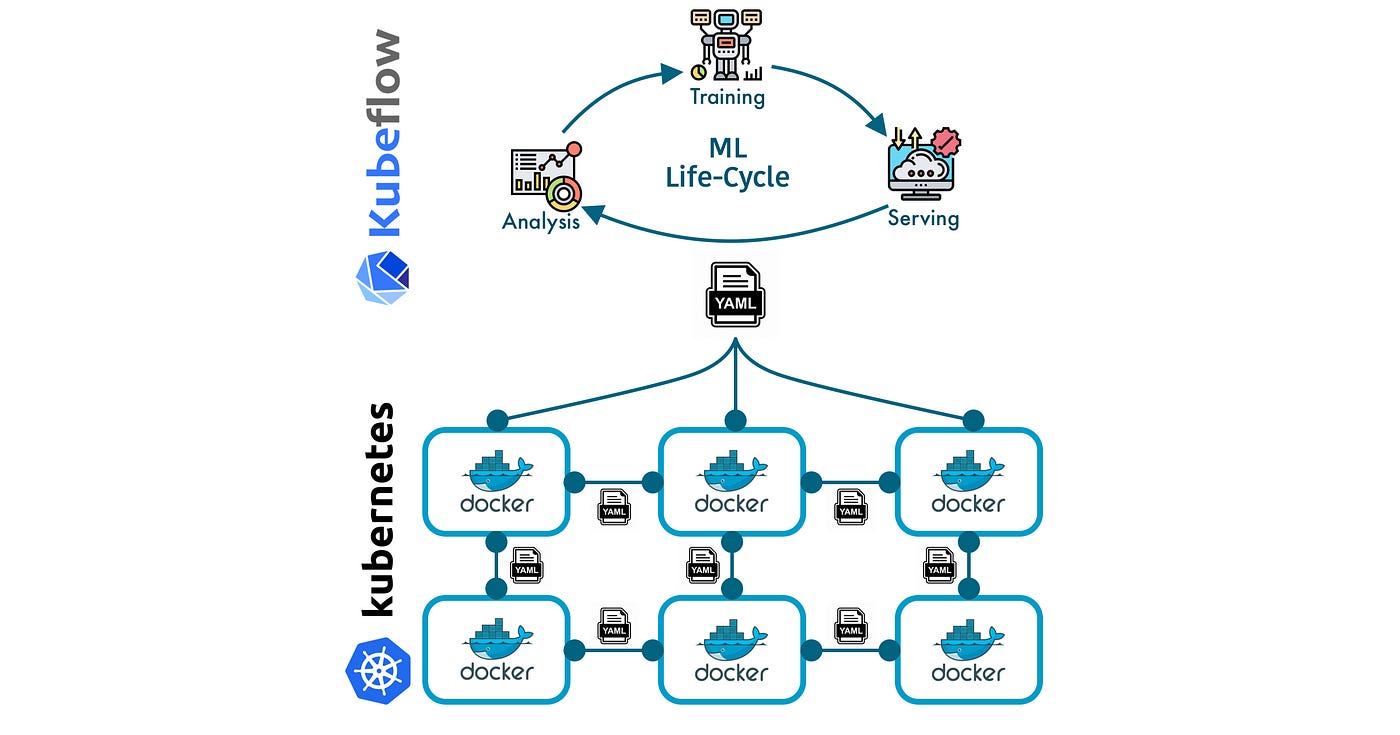
Kubeflow 是 google 开发的包含了机器学习模型开发生命周期的开源平台。 Kubeflow 由一组工具组成,这些工具解决了机器学习生命周期中的每个阶段,例如:数据探索、特征工程、特征转换、模型实验、模型训练、模型评估、模型调整、模型服务和 模型版本控制。 kubeflow 的主要属性是它被设计为在 kubernetes 之上工作,也就是说,kubeflow 利用了 kubernetes 集群提供的好处,例如容器编排和自动扩展。

Kubeflow components in the ML workflow

安装 kubeflow
下载 修改过镜像地址的的代码仓库
1
2
3
|
git clone https://github.com/zhuyaguang/manifests.git
while ! kustomize build example | kubectl apply -f -; do echo "Retrying to apply resources"; sleep 10; done
|
启动kubeflow界面
1
|
kubectl port-forward --address 0.0.0.0 -n istio-system svc/istio-ingressgateway 8080:80 &
|
kubeflow学习指南笔记
本书代码地址
设置镜像仓库
Kaniko配置指南:https://github.com/GoogleContainerTools/kaniko#pushing-to-different-registries
创建一个 kubeflow 项目,手写数字识别
模型查询示例代码: https://github.com/intro-to-ml-with-kubeflow/intro-to-ml-with-kubeflow-examples/blob/master/ch2/query-endpoint.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
import requests
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def download_mnist():
return input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
def gen_image(arr):
two_d = (np.reshape(arr, (28, 28)) * 255).astype(np.uint8)
plt.imshow(two_d, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
return plt
#end::scriptSetup[]
AMBASSADOR_API_IP = "10.53.148.167:30134"
#tag::scriptGuts[]
mnist = download_mnist()
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(1)
chosen = 0
gen_image(batch_xs[chosen]).show()
data = batch_xs[chosen].reshape((1, 784))
features = ["X" + str(i + 1) for i in range(0, 784)]
request = {"data": {"names": features, "ndarray": data.tolist()}}
deploymentName = "mnist-classifier"
uri = "http://" + AMBASSADOR_API_IP + "/seldon/" + \
deploymentName + "/api/v0.1/predictions"
response = requests.post(uri, json=request)
#end::scriptGuts[]
print(response.status_code)
|
kubeflow 组件设计
Central Dashboard :主界面
Kubeflow Notebooks:可以安装Jupyter
Kubeflow Pipelines:pipeline
Katib:超参数调优
Training Operators:各种训练模型的 crd controller
Multi-Tenancy :多租户
Pipeline
pipeline本质上是一个容器执行的图,除了指定哪些容器以何种顺序运行之外,它还允许用户向整个pipeline传递参数和在容器之间传递参数。
每一个pipeline包含下面四个必要步骤
1.创建容器 2.创建一个操作 3.对操作进行排序 4.输出为可执行的YAML文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
from kfp import dsl, compiler
import kfp as comp
@comp.create_component_from_func
def echo_op():
print("Hello world")
@dsl.pipeline(
name='my-first-pipeline',
description='A hello world pipeline.'
)
def hello_world_pipeline():
echo_task = echo_op()
if __name__ == '__main__':
compiler.Compiler().compile(hello_world_pipeline, __file__ + '.yaml')
|
pipeline 基本例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
import kfp
from kfp import compiler
import kfp.dsl as dsl
import kfp.notebook
import kfp.components as comp
#Define a Python function
def add(a: float, b: float) -> float:
'''Calculates sum of two arguments'''
return a + b
add_op = comp.func_to_container_op(add)
from typing import NamedTuple
def my_divmod(
dividend: float, divisor: float
) -> NamedTuple('MyDivmodOutput', [('quotient', float), ('remainder', float)]):
'''Divides two numbers and calculate the quotient and remainder'''
#Imports inside a component function:
import numpy as np
#This function demonstrates how to use nested functions inside a component function:
def divmod_helper(dividend, divisor):
return np.divmod(dividend, divisor)
(quotient, remainder) = divmod_helper(dividend, divisor)
from collections import namedtuple
divmod_output = namedtuple('MyDivmodOutput', ['quotient', 'remainder'])
return divmod_output(quotient, remainder)
divmod_op = comp.func_to_container_op(
my_divmod, base_image='tensorflow/tensorflow:1.14.0-py3')
@dsl.pipeline(
name='Calculation pipeline',
description='A toy pipeline that performs arithmetic calculations.')
def calc_pipeline(
a='a',
b='7',
c='17',
):
#Passing pipeline parameter and a constant value as operation arguments
add_task = add_op(a, 4) # Returns a dsl.ContainerOp class instance.
#Passing a task output reference as operation arguments
#For an operation with a single return value, the output reference can be accessed using `task.output` or `task.outputs['output_name']` syntax
divmod_task = divmod_op(add_task.output, b)
#For an operation with a multiple return values, the output references can be accessed using `task.outputs['output_name']` syntax
result_task = add_op(divmod_task.outputs['quotient'], c)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Compiling the pipeline
kfp.compiler.Compiler().compile(calc_pipeline, 'ch04.yaml')
|
步骤之间存储数据
kubeflow Pipeline 的 volumeOp 允许创建一个自动管理的持久卷。
1
|
dvop = dsl.volumeOp(name="create_pvc",resource_name="my-pvc-2",size="5Gi",modes=dsl.VOLUME_MODE_RWO)
|
还可以利用 MinIO 把文件写入容器本地,并在ContainerOp中指定参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
fetch = kfp.dsl.ContainerOp(
name="download",
command=['sh','-c'],
arguments=[
'sleep 1;'
'mkdir -p /tmp/data;'
'wget '+ data_url +' -O /tmp/data/result.csv'
],
file_outputs={'downloaded':'/tmp/data'}
)
|
pipeline 之间传递数据例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
from ast import arguments
from unicodedata import name
from setuptools import Command
from kfp import dsl, compiler
def gcs_download_op(url):
return dsl.ContainerOp(
name='GCS - Download',
image='google/cloud-sdk:279.0.0',
command=['sh', '-c'],
arguments=['gsutil cat $0 | tee $1', url, '/tmp/results.txt'],
file_outputs={
'data': '/tmp/results.txt',
}
)
def echo_op(text):
return dsl.ContainerOp(
name='echo',
image='library/bash:4.4.23',
command=['sh', '-c'],
arguments=['echo "$0"', text]
)
@dsl.pipeline(
name='sequential-pipeline',
description='A pipeline with two sequential steps.'
)
def sequential_pipeline(url='gs://ml-pipeline/sample-data/shakespeare/shakespeare1.txt'):
"""A pipeline with two sequential steps."""
download_task = gcs_download_op(url)
echo_task = echo_op(download_task.output)
if __name__ == '__main__':
compiler.Compiler().compile(sequential_pipeline, __file__ + '.yaml')
|
func_to_container
一个函数变成一个container,有很多种方式
1.参数加镜像模式,业务逻辑通过镜像传递进来
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
def SendMsg(
send_msg: str = 'akash'
):
return dsl.ContainerOp(
name = 'Print msg',
image = 'docker.io/akashdesarda/comp1:latest', #逻辑在这里面
command = ['python', 'msg.py'],
arguments=[
'--msg', send_msg
],
file_outputs={
'output': '/output.txt',
}
)
|
2.参数加函数模式加基础镜像,业务逻辑直接写在函数里面,通过基础镜像运行 有bug,会去拉busybox镜像,需要修改源代码的基础镜像。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
def load_data(log_folder:str)->NamedTuple('Outputs', [('start_time_string',str)]):
# some code here
#逻辑在这里面
load_data_op=func_to_container_op(
func=load_data,
base_image="mike0355/k8s-facenet-distributed-training:4",
)
|
3.目前最新的版本似乎都提倡LoadFrom File/URL/Text这种形式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
import kfp
import kfp.components as comp
import kfp.dsl as dsl
create_step_get_lines = comp.load_component_from_text("""
name: Get Lines
description: Gets the specified number of lines from the input file.
inputs:
- {name: input_1, type: String, description: 'Data for input_1'}
- {name: parameter_1, type: Integer, default: '100', description: 'Number of lines to copy'}
outputs:
- {name: output_1, type: String, description: 'output_1 data.'}
implementation:
container:
image: zhuyaguang/pipeline:v4
command: [
python3,
# Path of the program inside the container
/pipelines/component/src/v2_2.py,
--input1-path,
{inputPath: input_1},
--param1,
{inputValue: parameter_1},
--output1-path,
{outputPath: output_1},
]""")
# Define your pipeline
@dsl.pipeline(
pipeline_root='',
name="example-pipeline",
)
def my_pipeline():
get_lines_step = create_step_get_lines(
# Input name "Input 1" is converted to pythonic parameter name "input_1"
input_1='one\ntwo\nthree\nfour\nfive\nsix\nseven\neight\nnine\nten',
parameter_1='5',
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Compiling the pipeline
kfp.compiler.Compiler().compile(my_pipeline, 'v2.yaml')
|
更多的方式例子可参考:标准组件库
Pipeline 高级主题
- 复杂条件判断
- 定期执行pipeline,使用recurring
数据准备和特征准备
2022数据准备工具列表
元数据
ML Metadata
使用TFjob训练机器学习模型(预测用户购买行为)
用户购买记录数据
Notebook 基础镜像:tensorflow-1.15.2-notebook-cpu:1.0.0
1
2
3
4
|
wget http://dl.minio.org.cn/client/mc/release/linux-amd64/mc //该地址已经404了
https://dl.min.io/client/mc/release/linux-amd64/
chmod +x mc
./mc --help
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
kubectl port-forward --address 0.0.0.0 -n kubeflow svc/minio-service 9000:9000 &
./mc config host add minio http://10.101.32.13:9000 minio minio123
./mc mb minio/data
./mc cp recommend_1.csv minio/data/recommender/user.csv
./mc cp trx_data.csv minio/data/recommender/transations.csv
|
-
创建notebook,并进行 tensorflow 训练
使用 public.ecr.aws/j1r0q0g6/notebooks/notebook-servers/jupyter:v1.5.0 作为base镜像
训练代码地址
-
部署 tensorflow 作业,使用TFJobs,把训练代码放置容器里面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
FROM tensorflow/tensorflow:1.15.0-py3
RUN pip3 install --upgrade pip
RUN pip3 install pandas --upgrade
RUN pip3 install keras --upgrade
RUN pip3 install minio --upgrade
RUN pip3 install kubernetes --upgrade
RUN pip3 install kfmd --upgrade
RUN mkdir -p /opt/kubeflow
COPY Recommender_Kubeflow.py /opt/kubeflow/
ENTRYPOINT ["python3", "/opt/kubeflow/Recommender_Kubeflow.py"]
|
1
|
docker build -t kubeflow/recommenderjob:1.0 .
|
TFJob.yaml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
apiVersion: kubeflow.org/v1
kind: TFJob
metadata:
name: recommenderjob
namespace: kubeflow-user-example-com
spec:
tfReplicaSpecs:
Worker:
replicas: 1
restartPolicy: Never
template:
metadata:
annotations:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
spec:
containers:
- name: tensorflow
image: 10.100.29.62/kubeflow/recommender:1.0
imagePullSecrets:
- name: harbor
|
更多的TFJob 和 PyTorchJob 可以参考文档 来进行更详细的配置和使用GPU、TPU等不同的硬件。
使用PyTorchJob训练机器学习模型 (孙浩的专利检索)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
# In[ ]:
from transformers import (
BertConfig,
BertTokenizer,
BertForMaskedLM,
LineByLineTextDataset,
DataCollatorForLanguageModeling,
Trainer,
TrainingArguments
)
import torch
import tokenizers
import argparse
def main(args):
tokenizer_kwargs = {
"model_max_length": 512
}
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('/home/pipeline-demo/', **tokenizer_kwargs)
config_new = BertConfig.from_pretrained(args.config)
model = BertForMaskedLM.from_pretrained(args.model, config=config_new)
model.resize_token_embeddings(len(tokenizer))
train_dataset = LineByLineTextDataset(tokenizer = tokenizer,file_path = args.file_path, block_size=512)
data_collator = DataCollatorForLanguageModeling(tokenizer=tokenizer, mlm=True, mlm_probability=0.15)
pretrain_batch_size=16
num_train_epochs=5
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir='/home/pipeline-demo/args', overwrite_output_dir=True, num_train_epochs=num_train_epochs,
learning_rate=1e-4, weight_decay=0.01, warmup_steps=10000, local_rank = args.local_rank, #dataloader_pin_memory = False,
per_device_train_batch_size=pretrain_batch_size, logging_strategy ="epoch",save_strategy = "epoch", save_total_limit = 1)
trainer = Trainer(
model=model, args=training_args, data_collator=data_collator, train_dataset=train_dataset)
trainer.train()
trainer.save_model(args.save_dir)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="nezha_train")
parser.add_argument("--config", type = str, default = "bert-base-uncased", help = "二次训练_nezha")
parser.add_argument("--model", type = str, default = "bert-base-uncased", help = "二次训练_nezha")
parser.add_argument("--file_path", type = str, default = "/home/pipeline-demo/newfileaa", help = "二次训练_nezha")
parser.add_argument("--save_dir", type = str, default = "/home/pipeline-demo", help = "二次训练_nezha")
parser.add_argument("--local_rank", type = int, default = -1, help = "For distributed training: local_rank")
args = parser.parse_args()
main(args)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
FROM python:3.7
RUN python3 -m pip install transformers
RUN python3 -m pip install torch -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
RUN python3 -m pip install tokenizers
RUN python3 -m pip install argparse
COPY ./vocab.txt /home/pipeline-demo/vocab.txt
COPY ./newfileaa /home/pipeline-demo/newfileaa
COPY ./train.py /home/pipeline-demo/train.py
|
1
|
docker build -f Dockerfile -t 10.100.29.62/kubeflow/train:v2 ./
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
apiVersion: "kubeflow.org/v1"
kind: PyTorchJob
metadata:
name: pytorch-simple
namespace: kubeflow
spec:
pytorchReplicaSpecs:
Master:
replicas: 1
restartPolicy: OnFailure
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: pytorch
image: 10.100.29.62/kubeflow/train:v2
imagePullPolicy: Always
command:
- "python3"
- "/home/pipeline-demo/train.py"
Worker:
replicas: 1
restartPolicy: OnFailure
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: pytorch
image: 10.100.29.62/kubeflow/train:v2
imagePullPolicy: Always
command:
- "python3"
- "/home/pipeline-demo/train.py"
|
问题